The regulatory role of AT 1 receptor on activated HSCs in hepatic fibrogenesis:effects of RAS inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl(4)
- PMID: 11819703
- PMCID: PMC4728269
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i6.824
The regulatory role of AT 1 receptor on activated HSCs in hepatic fibrogenesis:effects of RAS inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl(4)
Abstract
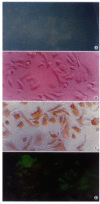
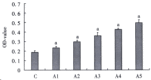
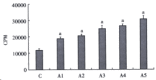
AIM:To assess the effect of ACE inhibitor and Ang II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist in preventing hepatic fibrosis caused by CCl(4) administration in rats;to investigate whether or not there are expression of AT 1 receptors on hepatic stellate cells; and to observe the effect of Ang II on proliferation and ECM synthesis of cultured HSCs.METHODS:Studies were conducted in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Except for the hepatofibrotic model group and the control group, in three treated groups, either enalapril (5mg/kg), or losartan (10mg/kg), or enalapril + losartan were given to the fibrotic rats by daily gavage, and saline vehicle was given to model and normal control rats. After 6 weeks, liver fibrosis was assessed directly by hepatic morphometric analysis, which has been considered the gold standard for the quantification of fibrosis. The expressions of AT 1 receptors and (alpha-mooth muscle actin,alpha-SMA) in liver tissue or isolated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were detected by immunohistochemical techniques. The effect of Ang II on HSC proliferation was determined by MTT method. Effect of Ang II on collagen synthesis of HSCs was determined by (3)H-proline incorporation.RESULTS:Contrasted to the fibrosis in rats of the model group, groups of rats treated with either enalapril or losartan, or a combination of two drugs showed a limited expansion of the interstitium (4.23 plus minus 3.70 vs 11.22 plus minus 4.79, P<0.05), but no difference was observed among three treated groups (5.38 plus minus3.43, 4.96 plus minus 2.96, 4.23 plus minus 2.70, P>0.05). Expression of AT 1 receptors was found in fibrotic interstitium of fibrotic rats, whereas in normal control rats they were limited to vasculature only to a very slight degree. AT 1 receptors were also expressed on activated HSCs in the culture. At concentrations from 10(-9) to 10(-5)mol/L, Ang II stimulated HSC proliferation in culture in a dose dependent manner. Increasing Ang II concentrations produced corresponding increases in (3)H-proline incorporation. Differences among groups were significant.CONCLUSION:Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and AT 1 blocker may slow the progression of hepatic fibrosis;activated HSCs express AT 1 receptors, and Ang II can stimulate the proliferation and collagen synthesis of HSCs in a dose-dependent manner; and activation of RAS may be related to hepatic fibrogenesis induced by CCl(4).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The expression of AT1 receptor on hepatic stellate cells in rat fibrosis induced by CCl4.Chin Med J (Engl). 2001 Jun;114(6):583-7. Chin Med J (Engl). 2001. PMID: 11780431
-
Effects of AT1 receptor antagonist, losartan, on rat hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl(4).World J Gastroenterol. 2000 Aug;6(4):540-545. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i4.540. World J Gastroenterol. 2000. PMID: 11819643 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of angiotensin II and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist on the proliferation, contraction and collagen synthesis in rat hepatic stellate cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2008 Jan 20;121(2):161-5. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008. PMID: 18272044
-
Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits angiotensin II-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells associated with interference of platelet-derived growth factor β receptor pathways.FEBS J. 2014 Jun;281(12):2754-68. doi: 10.1111/febs.12818. Epub 2014 May 16. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24725506
-
New Drugs for Hepatic Fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 13;13:874408. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.874408. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35770089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on experimental hepatic fibrogenesis.Dig Dis Sci. 2008 Mar;53(3):789-93. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9941-y. Epub 2007 Sep 1. Dig Dis Sci. 2008. PMID: 17763951
-
Activation of the renin-angiotensin system stimulates biliary hyperplasia during cholestasis induced by extrahepatic bile duct ligation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Apr 15;308(8):G691-701. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00116.2014. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25678505 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental study of effect of Ganyanping on fibrosis in rat livers.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jun;9(6):1292-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1292. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12800243 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen reduces CCL4- induced liver fibrosis in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Oct;8(5):883-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.883. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12378635 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic effects of tranilast on proliferation and collagen synthesis induced by TGF-beta2 in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2004;24(5):490-2, 496. doi: 10.1007/BF02831117. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2004. PMID: 15641701
References
-
- Yin F, Yao SK, Li ZH, Shi HC. Study on the therapeutic effect of all-trans retinoic acid and malotilate on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis of rats. World J Gastroenterol. 1998;4(Suppl 2):99.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

