Hepatitis C virus in human B lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus in vitro by in situ reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
- PMID: 11819792
- PMCID: PMC4688724
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.370
Hepatitis C virus in human B lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus in vitro by in situ reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
Abstract
Aim: To study persistence and replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in patients' peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) cultured in vitro.
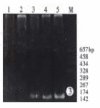
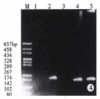
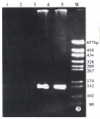
Methods: Epstein Barr virus (EBV) was used to transform the hepatitis C virus from a HCV positive patient to permanent lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL). Positive and negative HCV RNA strands of the cultured cells and growth media were detected by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) each month. Core and NS5 proteins of HCV were further tested using immunohistochemical SP method and in situ RT-PCR.
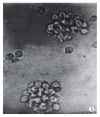
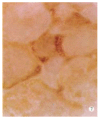
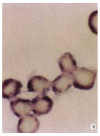
Results: HCV RNA positive strands were consistently detected the cultured cells for one year. The negative-strand RNA in LCL cells and the positive-strand RNA in supernatants were observed intermittently. Immunohistochemical results medicated expression of HCV NS3 and C proteins in LCL cytoplasm mostly. The positive signal of PCR product was dark blue and mainly localized to the LCL cytoplasm. The RT-PCR signal was eliminated by overnight RNase digestion but not DNase digestion.
Conclusion: HCV may exist and remain functional in a cultured cell line for a long period.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Persistence of hepatitis C virus type II in patient's peripheral blood B lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2000 May;80(5):349-53. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2000. PMID: 11798785 Chinese.
-
[Establishment of hepatitis C virus reproductive model of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus].Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 1999 Sep 30;13(3):280-3. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 1999. PMID: 12569765 Chinese.
-
Detection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) negative strand RNA and NS3 protein in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC): CD3+, CD14+ and CD19+.Virol J. 2013 Nov 26;10:346. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-346. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 24279719 Free PMC article.
-
In situ reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction: an innovative tool for hepatitis C virus RNA detection and localisation, and for quantification of infected cells.Eur J Histochem. 1998;42(2):133-6. Eur J Histochem. 1998. PMID: 9728290 Review.
-
Human cell types important for hepatitis C virus replication in vivo and in vitro: old assertions and current evidence.Virol J. 2011 Jul 11;8:346. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-346. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 21745397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus in hepatocellular carcinogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Dec 1;10(23):3409-13. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3409. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15526357 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of human single chain Fv antibody against hepatitis C virus E2 protein and its identification in immunohistochemistry.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Oct;8(5):863-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.863. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12378631 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference: antiviral weapon and beyond.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Aug;9(8):1657-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1657. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12918096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methodologic research on TIMP-1, TIMP-2 detection as a new diagnostic index for hepatic fibrosis and its significance.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Apr;8(2):282-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i2.282. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 11925608 Free PMC article.
-
HCV replication in PBMC and its influence on interferon therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Feb;9(2):291-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.291. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12532451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaito M, Watanabe S, Tsukiyama-Kohara K, Yamaguchi K, Kobayashi Y, Konishi M, Yokoi M, Ishida S, Suzuki S, Kohara M. Hepatitis C virus particle detected by immunoelectron microscopic study. J Gen Virol. 1994;75(Pt 7):1755–1760. - PubMed
-
- Gastaldi M, Massacrier A, Planells R, Robaglia-Schlupp A, Portal-Bartolomei I, Bourlière M, Quilici F, Fiteni J, Mazzella E, Cau P. Detection by in situ hybridization of hepatitis C virus positive and negative RNA strands using digoxigenin-labeled cRNA probes in human liver cells. J Hepatol. 1995;23:509–518. - PubMed
-
- Houghton M, Weiner A, Han J, Kuo G, Choo QL. Molecular biology of the hepatitis C viruses: implications for diagnosis, development and control of viral disease. Hepatology. 1991;14:381–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

