Establishment of cell clones with different metastatic potential from the metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line MHCC97
- PMID: 11819844
- PMCID: PMC4695564
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.630
Establishment of cell clones with different metastatic potential from the metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line MHCC97
Abstract
Aim: To establish clone cells with different metastatic potential for the study of metastasis-related mechanisms.
Methods: Cloning procedure was performed on parental hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line MHCC97, and biological characteristics of the target clones selected by in vivo screening were studied.
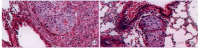
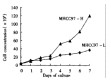
Results: Two clones with high (MHCC97-H) and low (MHCC97-L) metastatic potential were isolated from the parent cell line. Compared with MHCC97-L, MHCC97-H had smaller cell size (average cell diameter 43 microm vs 50 microm) and faster in vitro and in vivo growth rate (tumor cell doubling time was 34.2h vs 60.0h). The main ranges of chromosomes were 55-58 in MHCC97-H and 57-62 in MHCC97-L. Boyden chamber in vitro invasion assay demonstrated that the number of penetrating cells through the artificial basement membrane was (37.5 +/- 11.0) cells/field for MHCC97-H vs (17.7 +/- 6.3)/field for MHCC97-L. The proportions of cells in G0-G1 phase, S phase, and G2-M phase for MHCC97-H/MHCC97-L were 0.56/0.65, 0.28/0.25 and 0.16/0.10, respectively, as measured by flow cytometry. The serum AFP levels in nude mice 5wk after orthotopic implantation of tumor tissue were (246 +/- 66) microg.L(-1) for MHCC97-H and (91 +/- 66) microg.L(-1) for MHCC97-L. The pulmonary metastatic rate was 100% (10/10) vs 40% (4/10).
Conclusion: Two clones of the same genetic background but with different biological behaviors were established, which could be valuable models for investigation on HCC metastasis.
Figures



Comment in
-
Moving toward an understanding of the metastatic process in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Dec;7(6):777-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.777. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11854899 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fidler IJ. Tumor heterogeneity and the biology of cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 1978;38:2651–2660. - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6130–6138. - PubMed
-
- Maekawa R, Kishimoto Y, Sato K, Homma M. Establishment of highly metastatic tumor clones derived from a skin squamous cell carcinoma (SqC-NH), D-1 and F-3, with distinct features of pulmonary metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1993;11:343–353. - PubMed
-
- Navone NM, Olive M, Ozen M, Davis R, Troncoso P, Tu SM, Johnston D, Pollack A, Pathak S, von Eschenbach AC, et al. Establishment of two human prostate cancer cell lines derived from a single bone metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:2493–2500. - PubMed
-
- Dexter DL, Spremulli EN, Fligiel Z, Barbosa JA, Vogel R, VanVoorhees A, Calabresi P. Heterogeneity of cancer cells from a single human colon carcinoma. Am J Med. 1981;71:949–956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

