Salt intake, endothelial dysfunction, and salt-sensitive hypertension
- PMID: 11821636
- PMCID: PMC8101840
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2002.00503.x
Salt intake, endothelial dysfunction, and salt-sensitive hypertension
Abstract
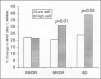
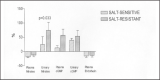
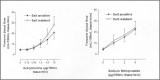
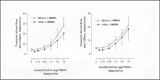
Numerous epidemiologic and clinical studies have demonstrated a clear relationship between high salt intake and blood pressure. However, the mechanisms of a salt-induced increase in blood pressure--a phenomenon known as salt sensitivity--and the heterogeneity of this effect are far from being completely understood. Endothelial dysfunction, and especially the nitric oxide system, is implicated in both experimental and clinical hypertension. Animal studies indicate that endogenous nitric oxide plays an important role in renal hemodynamics and sodium homeostasis, inducing renal vasodilation and natriuresis. Studies of essential hypertensive patients have also suggested that both high salt intake and salt sensitivity are associated with impaired endothelial function. Although there are many hypotheses concerning the nature of salt sensitivity, clinical data indicate that salt-sensitive patients may be unable to up-regulate the production of nitric oxide in response to salt intake. This endothelial dysfunction, which is more frequent in salt-sensitive than in salt-resistant essential hypertensive patients, may partially explain the blood pressure increase in response to salt intake and may underlie the more pronounced target organ damage and cardiovascular risk in salt-sensitive patients.
(c) 2002 Le Jacq Communications, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Hormonal profile and participation of nitric oxide in salt-sensitive and salt-resistant essential arterial hypertension].Nefrologia. 2000 Sep-Oct;20(5):415-23. Nefrologia. 2000. PMID: 11100662 Spanish.
-
The blood pressure-salt sensitivity paradigm: pathophysiologically sound yet of no practical value.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016 Sep;31(9):1386-91. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw295. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27521374
-
Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis determines sensitivity to the pressor effect of salt.Kidney Int. 1994 Jul;46(1):230-6. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.264. Kidney Int. 1994. PMID: 7523754
-
Novel Paradigms of Salt and Hypertension.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 May;28(5):1362-1369. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016080927. Epub 2017 Feb 20. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28220030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:61-84. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_147. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27757935 Review.
Cited by
-
Recommendation of low-salt diet and short-term outcomes in heart failure with preserved systolic function.Am J Med. 2009 Nov;122(11):1029-36. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.04.025. Am J Med. 2009. PMID: 19854331 Free PMC article.
-
Role of "Western diet" in inflammatory autoimmune diseases.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014 Jan;14(1):404. doi: 10.1007/s11882-013-0404-6. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014. PMID: 24338487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional foods for augmenting nitric oxide activity and reducing the risk for salt-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease in Japan.J Cardiol. 2018 Jul;72(1):42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29544657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical Effects of Aqueous Extract of Persea americana (Mill) on the Myocardium of Left Ventricle of High Salt-Fed Adult Wistar Rats.J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2017 Oct;22(4):765-769. doi: 10.1177/2156587217733884. Epub 2017 Oct 5. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 29228805 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nitric Oxide in the Micro- and Macrovascular Response to a 7-Day High-Salt Diet in Healthy Individuals.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7157. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087157. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muntzel M, Drüeke T. A comprehensive review of the salt and blood pressure relationship. Am J Hypertens. 1992; 5:1S–42S. - PubMed
-
- Campese VM. Salt sensitivity in hypertension. Renal and cardiovascular implications. Hypertension. 1994;23: 531–550 - PubMed
-
- Weinberger MH. Salt sensitivity of blood pressure in humans. Hypertension. 1996;27:481–490. - PubMed
-
- Luft FC, Weinberger MH. Sodium sensitivity and resistance of blood pressure: the role of the kidney and the renin‐aldosterone axis. Kidney Int Suppl. 1987;22:S234–S241. - PubMed
-
- Giner V, Poch E, Bragulat E, et al. Renin‐angiotensin system genetic polymorphisms and salt sensitivity in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 2000;35:512–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

