Evidence of genetic interaction between the beta-globin complex and chromosome 8q in the expression of fetal hemoglobin
- PMID: 11822023
- PMCID: PMC384958
- DOI: 10.1086/339248
Evidence of genetic interaction between the beta-globin complex and chromosome 8q in the expression of fetal hemoglobin
Abstract
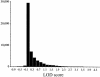
During human development, the switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin (Hb) is not complete with the residual gamma-globin expression being restricted to a subset of erythrocytes termed "F cells" (FC). Statistical analyses have shown the FC trait to be influenced by a common sequence variant (C-->T) at position -158 upstream of the Ggamma-globin gene, termed the "XmnI-Ggamma polymorphism." The XmnI-Ggamma site is believed to be involved in the expression of the Ggamma-globin gene through interaction with transcription factors, and polymorphisms in the transcription factors could be influencing fetal Hb expression, conditional on the XmnI-Ggamma site. Using a two-locus model, in which the second locus was the known quantitative-trait locus (QTL) at the XmnI-Ggamma site, we showed suggestive linkage to chromosome 8q. A maximum single-point LOD score of 4.33 and a multipoint LOD score of 4.75 were found in a 15-20 cM region of chromosome 8q. A single-locus analysis failed to show linkage of FC to the region when the XmnI-Ggamma site was accounted for by removing its effects from the data or including it as a covariate. Results of the single-locus analysis were significant when the effects of the XmnI-Ggamma site were not accounted for in any way. The results of analysis in a large Indian kindred indicate that there is an interaction between the XmnI-Ggamma site and a QTL on chromosome 8q that is influencing the production of fetal Hb.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative trait locus on chromosome 8q influences the switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin.Blood. 2004 Oct 1;104(7):2184-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0527. Epub 2004 Jun 17. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15205260
-
Developmental effect of the XmnI site on Ggamma-globin gene expression among newborn Hb F-Malta-I [Ggamma117(G19)His-->Arg, CAT-->CGT] heterozygotes and adult beta+ -Thalassemia homozygotes.Hemoglobin. 2007;31(1):71-82. doi: 10.1080/03630260601057187. Hemoglobin. 2007. PMID: 17365007
-
XmnI Ggamma-polymorphism in six unrelated Pakistani families with Inv/Del Ggamma(Agammadeltabeta) degrees deltabeta-thalassemia.Am J Hematol. 2005 Dec;80(4):303-5. doi: 10.1002/ajh.20376. Am J Hematol. 2005. PMID: 16315258
-
Genetic factors affecting clinical severity in beta-thalassemia syndromes.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2000 Nov-Dec;22(6):573-80. doi: 10.1097/00043426-200011000-00026. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2000. PMID: 11132233 Review.
-
Role of intergenic human gamma-delta-globin sequences in human hemoglobin switching and reactivation of fetal hemoglobin in adult erythroid cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1054:48-54. doi: 10.1196/annals.1345.057. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16339651 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Hemoglobinopathies: The Test Bench for Genome Editing-Based Therapeutic Strategies.Front Genome Ed. 2020 Dec 3;2:571239. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2020.571239. eCollection 2020. Front Genome Ed. 2020. PMID: 34713219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genetic and Clinical Significance of Fetal Hemoglobin Expression in Sickle Cell Disease.Med Princ Pract. 2021;30(3):201-211. doi: 10.1159/000511342. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Med Princ Pract. 2021. PMID: 32892201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-thalassaemia prototype of a single gene disorder with multiple phenotypes.Int J Hematol. 2002 Aug;76 Suppl 2:96-104. doi: 10.1007/BF03165097. Int J Hematol. 2002. PMID: 12430908 Review.
-
Effect of Swiss-type heterocellular HPFH from XmnI-Gγ and HBBP1 polymorphisms on HbF, HbE, MCV and MCH levels in Thai HbE carriers.Int J Hematol. 2014 Mar;99(3):338-44. doi: 10.1007/s12185-014-1516-z. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Int J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24474642
-
Fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia.Blood. 2011 Jul 7;118(1):19-27. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-325258. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21490337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boyer SH, Belding TK, Margolet L, Noyes AN (1975) Fetal hemoglobin restriction to a few erythrocytes (F cells) in normal human adults. Science 188:361–363 - PubMed
-
- Craig JE, Rochette J, Fisher CA, Weatherall DJ, Marc S, Lathrop GM, Demenais F, Thein SL (1996) Dissecting the loci controlling fetal haemoglobin production on chromosomes 11p and 6q by the regressive approach. Nat Genet 12:58–64 - PubMed
-
- Craig JE, Sheerin SM, Barnetson R, Thein SL (1993) The molecular basis of HPFH in a British family identified by heteroduplex formation. Br J Haematol 84:106–110 - PubMed
-
- Dib C, Fauré S, Fizames C, Samson D, Drouot N, Vignal A, Millasseau P, Marc S, Hazan J, Seboun E, Lathrop M, Gyapay G, Morissette J, Weissenbach J (1996) A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature 380:152–154 - PubMed
-
- Dover GJ, Smith KD, Chang YC, Purvis S, Mays A, Meyers DA, Sheils C, Serjeant G (1992) Fetal hemoglobin levels in sickle cell disease and normal individuals are partially controlled by an X-linked gene located at Xp22.2. Blood 80:816–824 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

