Contrasting requirements for ubiquitylation during Fc receptor-mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis
- PMID: 11823418
- PMCID: PMC125844
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.3.251
Contrasting requirements for ubiquitylation during Fc receptor-mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis
Abstract
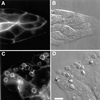
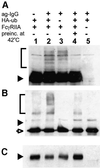
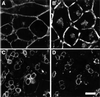
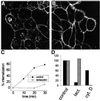
Fc receptors on leukocytes mediate internalization of antibody-containing complexes. Soluble immune complexes are taken up by endocytosis, while large antibody-opsonized particles are internalized by phagocytosis. We investigated the role of ubiquitylation in internalization of the human FcgammaRIIA receptor by endocytosis and phagocytosis. A fusion of FcgammaRIIA to green fluorescent protein (GFP) was expressed in ts20 cells, which bear a temperature-sensitive mutation in the E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme. Uptake of soluble IgG complexes mediated by FcgammaRIIA-GFP was blocked by incubation at the restrictive temperature, indicating that endocytosis requires ubiquitylation. In contrast, phagocytosis and phagosomal maturation were largely unaffected when ubiquitylation was impaired. FcgammaRIIA-GFP was ubiquitylated in response to receptor cross-linking. Elimination of the lysine residues present in the cytoplasmic domain of FcgammaRIIA impaired endocytosis, but not phagocytosis. The proteasomal inhibitor clasto-lactacystin beta-lactone strongly inhibited endocytosis, but did not affect phagocytosis. These studies demonstrate a role for ubiquitylation in the endocytosis of immune receptors, and reveal fundamental differences in the mechanisms underlying internalization of a single receptor depending on the size or multiplicity of the ligand complex.
Figures



References
-
- Cenciarelli C., Wilhelm,K.G.,Jr, Guo,A. and Weissman,A.M. (1996) T cell antigen receptor ubiquitination is a consequence of receptor-mediated tyrosine kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 8709–8713. - PubMed
-
- Daeron M. (1997) Fc receptor biology. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 15, 203–234. - PubMed
-
- Downey G.P., Botelho,R.J., Butler,J.R., Moltyaner,Y., Chien,P., Schreiber,A.D. and Grinstein,S. (1999) Phagosomal maturation, acidification and inhibition of bacterial growth in nonphagocytic cells transfected with FcγRIIA receptors. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 28436–28444. - PubMed
-
- Duchemin A.M., Ernst,L.K. and Anderson,C.L. (1994) Clustering of the high affinity Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G (FcγRI) results in phosphorylation of its associated γ-chain. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 12111–12117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

