Cryoglobulins
- PMID: 11825916
- PMCID: PMC1769573
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.55.1.4
Cryoglobulins
Abstract
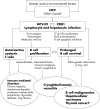
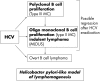
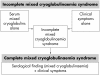
Serum cryoglobulins are found in a wide spectrum of disorders but are often transient and without clinical implications. Monoclonal cryoglobulins are usually associated with haematological disorders, whereas mixed cryoglobulins are found in many infectious and systemic disorders. So called essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia shows a striking association with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (> 90%). It is a systemic vasculitis (leucocytoclastic vasculitis) with cutaneous and multiple visceral organ involvement. Chronic HCV infection can lead to a constellation of autoimmune and neoplastic disorders. In this review, the aetiology, diagnosis, disease heterogeneity, and treatment of cryoglobulinaemia are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Wintrobe M, Buell M. Hyperproteinemia associated with multiple myeloma. With report of a case in which an extraordinary hyperproteinemia was associated with thrombosis of the retinal veins and symptoms suggesting Raynaud's disease. Bulletin of the John Hopkins Hospital 1933;52:156–65.
-
- Lospalluto J, Dorward B, Miller W, Jr, et al. Cryoglobulinemia based on interaction between a gamma macroglobulin and 7S gamma globulin. Am J Med 1962;32:142–5. - PubMed
-
- Middaugh CR, Litman GW. Atypical glycosylation of an IgG monoclonal cryoimmunoglobulin. J Biol Chem 1987;262:3671–3. - PubMed
-
- Tomana M, Schrohenloher RE, Koopman WJ, et al. Abnormal glycosylation of serum IgG from patients with chronic inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:333–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
