Comparative evaluation of the VERSANT HCV RNA 3.0, QUANTIPLEX HCV RNA 2.0, and COBAS AMPLICOR HCV MONITOR version 2.0 Assays for quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum
- PMID: 11825962
- PMCID: PMC153351
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.2.495-500.2002
Comparative evaluation of the VERSANT HCV RNA 3.0, QUANTIPLEX HCV RNA 2.0, and COBAS AMPLICOR HCV MONITOR version 2.0 Assays for quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum
Erratum in
- J Clin Microbiol 2002 May;40(5):1885
Abstract
A comparison of quantitative results expressed in hepatitis C virus (HCV) international units per milliliter, obtained from the VERSANT HCV RNA 3.0 (bDNA-3.0) assay, the QUANTIPLEX HCV RNA 2.0 (bDNA-2.0) assay, and the COBAS AMPLICOR HCV MONITOR version 2.0 (HCM-2.0) test was performed. A total of 168 patient specimens submitted to the Mayo Clinic Molecular Microbiology Laboratory for HCV quantification or HCV genotyping were studied. Of the specimens tested, 97, 88, and 79% yielded quantitative results within the dynamic range of the bDNA-3.0, bDNA-2.0, and HCM-2.0 assays, respectively. Overall, there was substantial agreement between the results generated by all three assays. A total of 15 out of 29 (52%) of the specimens determined to contain viral loads of <31,746 IU/ml by the bDNA-3.0 assay were categorized as containing viral loads within the range of 31,746 to 500,000 IU/ml by the bDNA-2.0 assay. Although substantial agreement was noted between the results generated by the bDNA-2.0 and bDNA-3.0 assays, a bias toward higher viral titer by the bDNA-2.0 assay was noted (P = 0.001). Likewise, although substantial agreement was noted between the results generated by the HCM-2.0 and bDNA-3.0 assays, a bias toward higher viral titer by the bDNA-3.0 assay was noted (P < or = 0.001). The discrepancy between the HCM-2.0 and bDNA-3.0 results was more pronounced when viral loads were >500,000 IU/ml and resulted in statistically significant differences (P < or = 0.001) in determining whether viral loads were above or below 800,000 IU/ml of HCV RNA, the proposed threshold value for tailoring the duration of combination therapy. The expression of quantitative values in HCV international units per milliliter was a strength of both the bDNA-3.0 and HCM-2.0 assays.
Figures
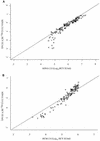
 , genotype 2; ▵, genotype 3; +, genotype 4; ◊, genotype 6; and ▿, genotype not determined.
, genotype 2; ▵, genotype 3; +, genotype 4; ◊, genotype 6; and ▿, genotype not determined.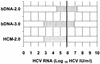
References
-
- Choo, Q. L., G. Kuo, A. J. Weiner, L. R. Overby, D. W. Bradley, and M. Houghton. 1989. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science 244:359-362. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, J. 1960. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales'. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 20:37-46.
-
- Collins, M. L., B. Irvine, D. Tyner, E. Fine, C. Zayati, C. Chang, T. Horn, D. Ahle, J. Detmer, L. P. Shen, J. Kolberg, S. Bushnell, M. S. Urdea, and D. D. Ho. 1997. A branched DNA signal amplification assay for quantification of nucleic acid targets below 100 molecules/ml. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:2979-2984. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davis, G. L., R. Esteban-Mur, V. Rustgi, J. Hoefs, S. C. Gordon, C. Trepo, M. L. Shiffman, S. Zeuzem, A. Craxi, M. H. Ling, and J. Albrecht. 1998. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of relapse of chronic hepatitis C. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 339:1493-1499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

