Neurogenesis in adult mammals: some progress and problems
- PMID: 11826089
- PMCID: PMC6758509
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-03-00619.2002
Neurogenesis in adult mammals: some progress and problems
Figures
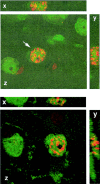
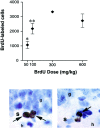
References
-
- Altman J. Are new neurons formed in the brains of adult mammals? Science. 1962;135:1127–1128. - PubMed
-
- Altman J. Autoradiographic investigation of cell proliferation in the brains of rats and cats. Postnatal growth and differentiation of the mammalian brain, with implications for a morphological theory of memory. Anat Rec. 1963;145:573–591. - PubMed
-
- Altman J. Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis II. A longitudinal investigation of the kinetics, migration and transformation of cells incorporating tritiated thymidine in infant rats, with special reference to postnatal neurogenesis in some brain regions. J Comp Neurol. 1966;128:431–474. - PubMed
-
- Altman J. Postnatal growth and differentiation of the mammalian brain, with implications for a morphological theory of memory. In: Quarton GC, Melnechuck T, Schmitt FO, editors. The neurosciences, a study program. Rockefeller UP; New York: 1967. pp. 723–743.
-
- Altman J. Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis IV. Cell proliferation and migration in the anterior forebrain, with special reference to persisting neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 1969;137:433–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
