Effects of irradiated medium with or without cells on bystander cell responses
- PMID: 11827706
- PMCID: PMC4041548
- DOI: 10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00285-8
Effects of irradiated medium with or without cells on bystander cell responses
Abstract
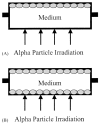
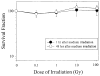
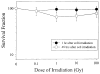
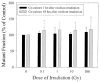
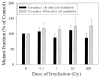
Recent studies have indicated that extranuclear or extracellular targets are important in mediating the bystander genotoxic effects of alpha-particles. In the present study, human-hamster hybrid (A(L)) cells were plated on either one or both sides of double-mylar dishes 2-4 days before irradiation, depending on the density requirement of experiments. One side (with or without cells) was irradiated with alpha-particles (from 0.1 to 100 Gy) using the track segment mode of a 4 MeV Van de Graaff accelerator. After irradiation, cells were kept in the dishes for either 1 or 48 h. The non-irradiated cells were then collected and assayed for both survival and mutation. When one side with cells was irradiated by alpha-particles (1, 10 and 100 Gy), the surviving fraction among the non-irradiated cells was significantly lower than that of control after 48 h co-culture. However, such a change was not detected after 1h co-culture or when medium alone was irradiated. Furthermore, co-cultivation with irradiated cells had no significant effect on the spontaneous mutagenic yield of non-irradiated cells collected from the other half of the double-mylar dishes. These results suggested that irradiated cells released certain cytotoxic factor(s) into the culture medium that killed the non-irradiated cells. However, such factor(s) had little effect on mutation induction. Our results suggest that different bystander end points may involve different mechanisms with different cell types.
Figures
References
-
- Nagasawa H, Little J. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges by extremely low doses of α-particles. Cancer Res. 1992;52:6394–6396. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande A, Goodwin EH, Bailey SM, Marrone BL, Lehnert BE. α-Particle-induced sister chromatid exchange in normal human lung fibroblasts: evidence for an extranuclear target. Radiat Res. 1996;145:260–267. - PubMed
-
- Prise KM, Belyakov OV, Folkard M, Michael BD. Studies of bystander effects in human fibroblasts using a charged particle microbeam. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998;74:793–798. - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa H, Little J. Unexpected sensitivity to the induction of mutations by very low doses of α-particle radiation: evidence for a bystander effect. Radiat Res. 1999;152:552–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

