Isotropic resolution diffusion tensor imaging with whole brain acquisition in a clinically acceptable time
- PMID: 11835610
- PMCID: PMC6871852
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.10018
Isotropic resolution diffusion tensor imaging with whole brain acquisition in a clinically acceptable time
Abstract
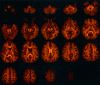
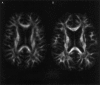
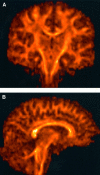
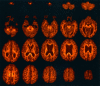
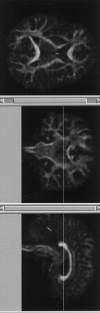
Our objective was to develop a diffusion tensor MR imaging pulse sequence that allows whole brain coverage with isotropic resolution within a clinically acceptable time. A single-shot, cardiac-gated MR pulse sequence, optimized for measuring the diffusion tensor in human brain, was developed to provide whole-brain coverage with isotropic (2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 mm) spatial resolution, within a total imaging time of approximately 15 min. The diffusion tensor was computed for each voxel in the whole volume and the data processed for visualization in three orthogonal planes. Anisotropy data were further visualized using a maximum-intensity projection algorithm. Finally, reconstruction of fiber-tract trajectories i.e., "tractography" was performed. Images obtained with this pulse sequence provide clear delineation of individual white matter tracts, from the most superior cortical regions down to the cerebellum and brain stem. Because the data are acquired with isotropic resolution, they can be reformatted in any plane and the sequence can therefore be used, in general, for macroscopic neurological or psychiatric neuroimaging investigations. The 3D visualization afforded by maximum intensity projection imaging and tractography provided easy visualization of individual white matter fasciculi, which may be important sites of neuropathological degeneration or abnormal brain development. This study has shown that it is possible to obtain robust, high quality diffusion tensor MR data at 1.5 Tesla with isotropic resolution (2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 mm) from the whole brain within a sufficiently short imaging time that it may be incorporated into clinical imaging protocols.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid whole-brain magnetic resonance imaging with isotropic resolution at 3 Tesla.Invest Radiol. 2009 Jan;44(1):54-9. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31818eee3c. Invest Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19060723
-
High spatial resolution nerve-specific DTI protocol outperforms whole-brain DTI protocol for imaging the trigeminal nerve in healthy individuals.NMR Biomed. 2021 Feb;34(2):e4427. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4427. Epub 2020 Oct 10. NMR Biomed. 2021. PMID: 33038059
-
Magnetic resonance tractography of the lumbosacral plexus: Step-by-step.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Feb 12;100(6):e24646. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024646. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33578590 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion-weighted MR of the brain: methodology and clinical application.Radiol Med. 2005 Mar;109(3):155-97. Radiol Med. 2005. PMID: 15775887 Review. English, Italian.
-
MR diffusion tensor imaging: recent advance and new techniques for diffusion tensor visualization.Eur J Radiol. 2003 Apr;46(1):53-66. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(02)00328-5. Eur J Radiol. 2003. PMID: 12648802 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial Gradient of Microstructural Changes in Normal-Appearing White Matter in Tracts Affected by White Matter Hyperintensities in Older Age.Front Neurol. 2019 Jul 25;10:784. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00784. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31404147 Free PMC article.
-
Structural differences in adolescent brains can predict alcohol misuse.Elife. 2022 May 26;11:e77545. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77545. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35616520 Free PMC article.
-
A Simplified Crossing Fiber Model in Diffusion Weighted Imaging.Front Neurosci. 2019 May 22;13:492. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00492. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31191215 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal evaluation of clinically early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis with diffusion tensor imaging.J Neurol. 2008 Mar;255(3):390-7. doi: 10.1007/s00415-008-0678-0. Epub 2008 Mar 20. J Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18350361
-
Spatial and orientational heterogeneity in the statistical sensitivity of skeleton-based analyses of diffusion tensor MR imaging data.J Neurosci Methods. 2011 Sep 30;201(1):213-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.07.025. Epub 2011 Jul 30. J Neurosci Methods. 2011. PMID: 21835201 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Atkinson D, Porter DA, Hill DL, Calamante F, Connelly A (2000): Sampling and reconstruction effects due to motion in diffusion‐weighted interleaved echo‐planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 44: 101–109. - PubMed
-
- Baratti C, Barnett AS, Pierpaoli C (1999): Comparative MR imaging study of brain maturation in kittens with T1, T2, and the trace of the diffusion tensor. Radiology 210: 133–142. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Matiello J, Le Bihan D (1994): Estimation of the effective self‐diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson Ser B 103: 247–254. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1995): Elucidating tissue structure by diffusion tensor MRI In: Book of abstracts: Third Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Vol. 2 Berkeley, CA: ISMRM; p 900.
-
- Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996): Microstructural and physiological features of tissue elucidated by quantitative‐diffusion‐tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111: 209–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

