Regional clustering of shared neutralization determinants on primary isolates of clade C human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from South Africa
- PMID: 11836401
- PMCID: PMC135941
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2233-2244.2002
Regional clustering of shared neutralization determinants on primary isolates of clade C human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from South Africa
Abstract
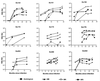
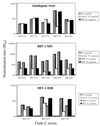
Clade C is one of the most prevalent genetic subtypes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in the world today and one of the least studied with respect to neutralizing antibodies. Most information on HIV-1 serology as it relates to neutralization is derived from clade B. Clade C primary isolates of HIV-1 from South Africa and Malawi were shown here to resemble clade B isolates in their resistance to inhibition by soluble CD4 and their sensitivity to neutralization by human monoclonal antibody immunoglobulin G1b12 and, to a lesser extent, 2F5. Unlike clade B isolates, however, all 16 clade C isolates examined resisted neutralization by 2G12. Infection with clade C HIV-1 in a cohort of female sex workers in South Africa generated antibodies that neutralized the autologous clade C isolate and T-cell-line-adapted (TCLA) strains of clade B. Neutralization of clade B TCLA strains was much more sensitive to the presence of autologous gp120 V3 loop peptides compared to the neutralization of clade C isolates in most cases. Thus, the native structure of gp120 on primary isolates of clade C will likely pose a challenge for neutralizing antibody induction by candidate HIV-1 vaccines much the same as it has for clade B. The autologous neutralizing antibody response following primary infection with clade C HIV-1 in South Africa matured slowly, requiring at least 4 to 5 months to become detectable. Once detectable, extensive cross-neutralization of heterologous clade C isolates from South Africa was observed, suggesting an unusual degree of shared neutralization determinants at a regional level. This high frequency of cross-neutralization differed significantly from the ability of South African clade C serum samples to neutralize clade B isolates but did not differ significantly from results of other combinations of clade B and C reagents tested in checkerboard assays. Notably, two clade C serum samples obtained after less than 2 years of infection neutralized a broad spectrum of clade B and C isolates. Other individual serum samples showed a significant clade preference in their neutralizing activity. Our results suggest that clades B and C are each comprised of multiple neutralization serotypes, some of which are more clade specific than others. The clustering of shared neutralization determinants on clade C primary HIV-1 isolates from South Africa suggests that neutralizing antibodies induced by vaccines will have less epitope diversity to overcome at a regional level.
Figures
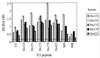
References
-
- Albert, J., B. Abrahamsson, K. Nagy, E. Aurelius, H. Gaines, G. Nystrom, and E. M. Fenyö. 1990. Rapid development of isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies after primary HIV-1 infection and consequent emergence of virus variants which resist neutralization by autologous sera. AIDS 4:107-112. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib, G., C. Combadiere, C. C. Broder, Y. Feng, P. E. Kennedy, P. M. Murphy, and E. A. Berger. 1996. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science 272:1955-1958. - PubMed
-
- Arendrup, M., C. Nielsen, J.-E. S. Hanson, C. Pedersen, L. Mathiesen, and J. O. Nielsen. 1992. Autologous HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies: emergence of neutralization-resistant escape virus and subsequent development of escape virus neutralizing antibodies. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 5:303-307. - PubMed
-
- Betts, M. R., J. Krowka, C. Santamaria, K. Balsamo, F. Gao, G. Mulundu, C. Luo, N. N’Gandu, H. Sheppard, B. H. Hahn, S. Allen, and J. A. Frelinger. 1997. Cross-clade human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in HIV-infected Zambians. J. Virol. 71:8908-8911. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

