Effectiveness of clozapine in neuroleptic-resistant schizophrenia: clinical response and plasma concentrations
- PMID: 11836974
- PMCID: PMC149793
Effectiveness of clozapine in neuroleptic-resistant schizophrenia: clinical response and plasma concentrations
Abstract
Objective: To assess the relation between plasma concentrations of clozapine and its 2 main metabolites desmethyl clozapine and clozapine N-oxide, and clinical change in a sample of inpatients with schizophrenia who were resistant to conventional neuroleptics.
Method: Thirty-seven patients (27 men and 10 women, mean age 34.8 yr) with treatment-resistant schizophrenia were treated with clozapine for 18 weeks; dosage was adjusted according to clinical response, and plasma concentrations of clozapine and of its metabolites were measured weekly by high-performance liquid chromatography. Clinical status was also assessed weekly with the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). Patients were considered "responsive" if they showed at least a 20% improvement over their baseline PANSS ratings.
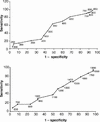
Results: The mean endpoint clozapine dosage was 486.5 mg/day. There was a significant correlation between the daily dosage of clozapine and the plasma levels of clozapine and of its metabolites (p < 0.05). There was no correlation between the clozapine plasma level and the percent improvement on the PANSS. Clozapine plasma levels were not significantly different between those who responded to clozapine (n = 19) and those who did not (n = 18) and were not significantly different between patients who smoked (n = 28) and those who did not (n = 9). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis determined the plasma level threshold (above which a better clinical response was obtained) to be 550 ng/mL. Using the total of plasma levels of clozapine and its metabolites did not lead to a better sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusions: Our calculated plasma clozapine threshold was higher than that reported by others, but this may be related to the severity of symptoms of our patient sample. Monitoring plasma rates remains a useful tool, together with clinical evaluation, to establish the clozapine dosage for an optimum benefit-risk ratio.
Objectif: Évaluer le lien entre les concentrations plasmatiques de clozapine et de ses deux principaux métabolites (desméthyl clozapine et clozapine N-oxyde) et les changements cliniques chez un échantillon de patients hospitalisés atteints de schizophrénie résistant aux neuroleptiques classiques.
Méthode: 37 patients (27 hommes et 10 femmes; âge moyen de 34,8 ans) atteints de schizophrénie réfractaire ont été traités à la clozapine pendant 18 semaines. On a rajusté la posologie en fonction de la réaction clinique et mesuré les concentrations plasmatiques de clozapine et de ses métabolites, la desméthyl clozapine et la clozapine N-oxyde, une fois par semaine par la chromatographie liquide à haut rendement. On a aussi évalué l'état clinique des sujets une fois par semaine en fonction de l'échelle des syndromes positifs et négatifs (PANSS). On a supposé que les patients « réagissaient » s'ils montraient une amélioration d'au moins 20 % par rapport à leurs résultats PANSS de référence.
Résultats: La posologie de virage moyenne de la clozapine s'est établie à 486,5 mg/jour. Il y avait un lien significatif entre la posologie quotidienne de clozapine et les concentrations plasmatiques de ses métabolites (p < 0,05). Il n'y avait pas de lien entre la concentration plasmatique de clozapine et le pourcentage d'amélioration selon l'échelle PANSS. Les concentrations plasmatiques de clozapine ne présentaient pas de différences significatives entre les sujets ayant réagi à la clozapine (n = 19) et ceux n'y ayant pas réagi (n = 18) et ne présentaient pas non plus de différence significative entre les patients fumeurs (n = 28) et non fumeurs (n = 9). L'analyse de la courbe des caractéristiques opérantes de l'opérateur (COO) a permis de déterminer que le seuil de concentration plasmatique (au-dessus duquel on obtient une meilleure réponse clinique) s'établit à 550 ng/mL. L'utilisation du total des concentrations plasmatiques de clozapine et de ses métabolites n'a pas produit de meilleurs taux de sensibilité et de spécificité.
Conclusions: Le seuil de concentration plasmatique de clozapine que nous avons calculé était plus élevé que celui dont d'autres chercheurs ont fait état, mais l'écart peut être relié à la gravité des symptômes chez nos patients. Le contrôle des concentrations plasmatiques est un moyen utile, conjugué à l'évaluation clinique, d'établir la posologie de clozapine nécessaire afin d'obtenir un ratio avantage-risque optimal.
Figures
References
-
- Hasegawa M, Gutierrez-Esteinou R, Way L, Meltzer HY. Relationship between clinical efficacy and clozapine concentrations in plasma in schizophrenia: effect of smoking. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1993;13:383-90. - PubMed
-
- Lane H, Chang Y, Chang W, Lin S, Tseng Y, Jann M. Effects of gender and age on plasma levels of clozapine and its metabolites analyzed by critical statistics. J Clin Psychiatry 1999;60:36-40. - PubMed
-
- Freeman DJ, Oyewumi LK. Will routine therapeutic drug monitoring have a place in clozapine therapy? Clin Pharmacokinet 1997;32:93-100. - PubMed
-
- Ackenheil VM, Brau H, Burkhart A, Franke A, Pacha W. Antipsychotic efficacy in relation to plasma levels of clozapine. Arneimittelforschung 1976;26:1156-8. - PubMed
-
- Thorup M, Fog R. Clozapine treatment of schizophrenic patients: plasma concentration and coagulation factor. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1977;66:123-6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical