Alveolar epithelial type I cells contain transport proteins and transport sodium, supporting an active role for type I cells in regulation of lung liquid homeostasis
- PMID: 11842214
- PMCID: PMC122303
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.042689399
Alveolar epithelial type I cells contain transport proteins and transport sodium, supporting an active role for type I cells in regulation of lung liquid homeostasis
Abstract
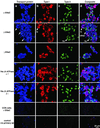
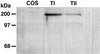
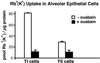
Transport of lung liquid is essential for both normal pulmonary physiologic processes and for resolution of pathologic processes. The large internal surface area of the lung is lined by alveolar epithelial type I (TI) and type II (TII) cells; TI cells line >95% of this surface, TII cells <5%. Fluid transport is regulated by ion transport, with water movement following passively. Current concepts are that TII cells are the main sites of ion transport in the lung. TI cells have been thought to provide only passive barrier, rather than active, functions. Because TI cells line most of the internal surface area of the lung, we hypothesized that TI cells could be important in the regulation of lung liquid homeostasis. We measured both Na(+) and K(+) (Rb(+)) transport in TI cells isolated from adult rat lungs and compared the results to those of concomitant experiments with isolated TII cells. TI cells take up Na(+) in an amiloride-inhibitable fashion, suggesting the presence of Na(+) channels; TI cell Na(+) uptake, per microgram of protein, is approximately 2.5 times that of TII cells. Rb(+) uptake in TI cells was approximately 3 times that in TII cells and was inhibited by 10(-4) M ouabain, the latter observation suggesting that TI cells exhibit Na(+)-, K(+)-ATPase activity. By immunocytochemical methods, TI cells contain all three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma) of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC and two subunits of Na(+)-, K(+)-ATPase. By Western blot analysis, TI cells contain approximately 3 times the amount of alphaENaC/microg protein of TII cells. Taken together, these studies demonstrate that TI cells not only contain molecular machinery necessary for active ion transport, but also transport ions. These results modify some basic concepts about lung liquid transport, suggesting that TI cells may contribute significantly in maintaining alveolar fluid balance and in resolving airspace edema.
Figures
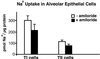

References
-
- Diamond J M. J Membr Biol. 1979;51:195–216. - PubMed
-
- Saumon G, Basset G. J Appl Physiol. 1993;74:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Matalon S, Benos D J, Jackson R M. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:L1–L22. - PubMed
-
- Matalon S, O'Brodovich H. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:627–661. - PubMed
-
- Weibel E R. Morphometry of the Human Lung. Berlin: Springer; 1963.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

