Disruption of primary auditory cortex by synchronous auditory inputs during a critical period
- PMID: 11842227
- PMCID: PMC122361
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261707398
Disruption of primary auditory cortex by synchronous auditory inputs during a critical period
Abstract
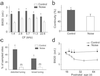
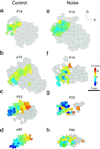
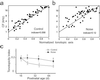
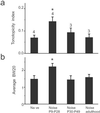
In the primary auditory cortex (AI), the development of tone frequency selectivity and tonotopic organization is influenced by patterns of neural activity. Introduction of synchronous inputs into the auditory pathway achieved by exposing rat pups to pulsed white noise at a moderate intensity during P9-P28 resulted in a disrupted tonotopicity and degraded frequency-response selectivity for neurons in the adult AI. The latter was manifested by broader-than-normal tuning curves, multipeaks, and discontinuous, tone-evoked responses within AI-receptive fields. These effects correlated with the severe impairment of normal, developmental sharpening, and refinement of receptive fields and tonotopicity. In addition, paradoxically weaker than normal temporal correlations between the discharges of nearby AI neurons were recorded in exposed rats. In contrast, noise exposure of rats older than P30 did not cause significant change of auditory cortical maps. Thus, patterned auditory inputs appear to play a crucial role in shaping neuronal processing/decoding circuits in the primary auditory cortex during a critical period.
Figures
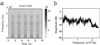


References
-
- Wiesel T N. Nature (London) 1982;299:583–591. - PubMed
-
- Penn A A, Shatz C J. Pediatr Res. 1999;45:447–458. - PubMed
-
- Katz L C, Shatz C J. Science. 1996;274:1133–1138. - PubMed
-
- Blakemore C, Cooper G F. Nature (London) 1970;228:477–478. - PubMed
-
- Sengpiel F, Stawinski P, Bonhoeffer T. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:727–732. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

