Mechanism of coupling of transport to hydrolysis in bacterial ATP-binding cassette transporters
- PMID: 11844750
- PMCID: PMC134847
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.5.1225-1233.2002
Mechanism of coupling of transport to hydrolysis in bacterial ATP-binding cassette transporters
Figures
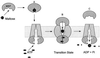

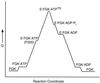
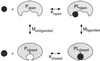
References
-
- Aleksandrov, L., A. Mengos, X. Chang, A. Aleksandrov, and J. R. Riordan. 2001. Differential interactions of nucleotides at the two nucleotide binding domains of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J. Biol. Chem. 276:12918-12923. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shawi, M. K., and A. E. Senior. 1993. Characterization of the adenosine triphosphatase activity of Chinese hamster P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:4197-4206. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shawi, M. K., I. L. Urbatsch, and A. E. Senior. 1994. Covalent inhibitors of P-glycoprotein ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 269:8986-8992. - PubMed
-
- Ames, G. F., C. S. Mimura, and V. Shyamala. 1990. Bacterial periplasmic permeases belong to a family of transport proteins operating from Escherichia coli to humans: traffic ATPases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 6:429-446. - PubMed
-
- Ames, G. F. L., C. E. Liu, A. K. Joshi, and K. Nikaido. 1996. Liganded and unliganded receptors interact with equal affinity with the membrane complex of periplasmic permeases, a subfamily of traffic ATPases. J. Biol. Chem. 271:14264-14270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

