Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-beta in annulus cells of the human intervertebral disc and the mitogenic effect of 17-beta-estradiol in vitro
- PMID: 11846890
- PMCID: PMC65546
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-3-4
Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-beta in annulus cells of the human intervertebral disc and the mitogenic effect of 17-beta-estradiol in vitro
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence suggests that estrogens exert effects in different tissues throughout the body, and that the estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) may be important for the action of estrogen (17-beta-estradiol) on the skeleton. The cellular localization of ERbeta in the human intervertebral disc, however, has not yet been explored.
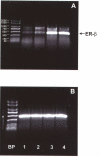
Methods: Human disc tissue and cultured human disc cells were used for immunocytochemical localization of ERbeta. mRNA was isolated from cultured human disc cells, and RT-PCR amplification of ERbeta was employed to document molecular expression of this receptor. Cultured human disc cells were tested to determine if 17-beta-estradiol stimulated cell proliferation.
Results: In this report data are presented which provide evidence for ERbeta gene expression in human intervertebral disc cells in vivo and in vitro. Culture of annulus cells in the presence of 10-7 M 17-beta-estradiol significantly increased cell proliferation.
Conclusions: These data provide new insight into the biology of cells in the annulus of the intervertebral disc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E1 and misoprostol increase epidermal growth factor production in 3D-cultured human annulus cells.Spine J. 2009 Sep;9(9):760-6. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2009.04.024. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19535298
-
Cortistatin is endogenous to the human intervertebral disc and exerts in vitro mitogenic effects on annulus cells and a downregulatory effect on TNF-α expression.Spine J. 2014 Dec 1;14(12):2995-3001. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24912122
-
The modulation of aromatase and estrogen receptor alpha in cultured human dermal papilla cells by dexamethasone: a novel mechanism for selective action of estrogen via estrogen receptor beta?J Invest Dermatol. 2006 Sep;126(9):2010-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700344. Epub 2006 May 11. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16691199
-
Leptin expression by annulus cells in the human intervertebral disc.Spine J. 2007 Jul-Aug;7(4):437-43. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2006.08.001. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Spine J. 2007. PMID: 17433782
-
Expression and functional roles of estrogen receptor GPR30 in human intervertebral disc.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Apr;158:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Jan 24. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26815911
Cited by
-
Protective effect of estrogen against calcification in the cartilage endplate.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Mar 1;11(3):1660-1666. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938266 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between hormone replacement therapy and spinal osteoarthritis: a nationwide health survey analysis of the elderly Korean population.BMJ Open. 2017 Nov 9;7(11):e018063. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018063. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29127229 Free PMC article.
-
17beta-estradiol Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Premature Senescence of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through Regulating the ROS/NF-κB Pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Jan 15;13(2):145-156. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.16770. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28255267 Free PMC article.
-
Intervertebral disc degeneration and how it leads to low back pain.JOR Spine. 2022 Nov 14;6(1):e1231. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1231. eCollection 2023 Mar. JOR Spine. 2022. PMID: 36994466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced ERbeta immunoexpression and apoptosis in the germ cells of cimetidine-treated rats.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009 Nov 18;7:127. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-127. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19922658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pelletier G. Localization of androgen and estrogen receptors in rat and primate tissues. Histol Histopathol. 2000;15:1261–1270. - PubMed
-
- Carson-Jurica MA, Schrader WT, O'Malley BW. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990;11:201–234. - PubMed
-
- Vidal O, Kindblom LG, Ohlsson C. Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-β in murine and human bone. J Bone Mineral Res. 1999;14:923–929. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

