Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-beta in annulus cells of the human intervertebral disc and the mitogenic effect of 17-beta-estradiol in vitro
- PMID: 11846890
- PMCID: PMC65546
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-3-4
Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-beta in annulus cells of the human intervertebral disc and the mitogenic effect of 17-beta-estradiol in vitro
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence suggests that estrogens exert effects in different tissues throughout the body, and that the estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) may be important for the action of estrogen (17-beta-estradiol) on the skeleton. The cellular localization of ERbeta in the human intervertebral disc, however, has not yet been explored.
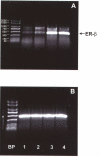
Methods: Human disc tissue and cultured human disc cells were used for immunocytochemical localization of ERbeta. mRNA was isolated from cultured human disc cells, and RT-PCR amplification of ERbeta was employed to document molecular expression of this receptor. Cultured human disc cells were tested to determine if 17-beta-estradiol stimulated cell proliferation.
Results: In this report data are presented which provide evidence for ERbeta gene expression in human intervertebral disc cells in vivo and in vitro. Culture of annulus cells in the presence of 10-7 M 17-beta-estradiol significantly increased cell proliferation.
Conclusions: These data provide new insight into the biology of cells in the annulus of the intervertebral disc.
Figures


References
-
- Pelletier G. Localization of androgen and estrogen receptors in rat and primate tissues. Histol Histopathol. 2000;15:1261–1270. - PubMed
-
- Carson-Jurica MA, Schrader WT, O'Malley BW. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990;11:201–234. - PubMed
-
- Vidal O, Kindblom LG, Ohlsson C. Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-β in murine and human bone. J Bone Mineral Res. 1999;14:923–929. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

