Cryptococcal choroid plexitis as a mass lesion: MR imaging and histopathologic correlation
- PMID: 11847053
- PMCID: PMC7975266
Cryptococcal choroid plexitis as a mass lesion: MR imaging and histopathologic correlation
Abstract
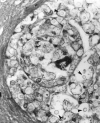
Cryptococcosis is a relatively common mycotic infection of the CNS caused by a ubiquitous saprophytic fungus. We present an unusual case of CNS cryptococcosis in an immunocompetent patient. Florid choroid plexitis resulted in the formation of intraventricular enhancing mass lesions that filled the ventricles and were hyperintense to associated periventricular edema on T2-weighted MR images. We also noted lesions corresponding to microcystic, dilated Virchow-Robin spaces in the basal ganglia that were characteristic of cryptococcal infection.
Figures


References
-
- Cho IC, Chang KH, Kim YH, Kim SH, Yu IK, Han MH. MR features of choroid plexitis. Neuroradiology 1998;40:303–307 - PubMed
-
- Hanly A, Petito CK. HLA–DR reactive dendritic cells of the human choroid plexus: a potential reservoir of HIV in the central nervous system. Hum Pathol 1998;29:88–93 - PubMed
-
- Davis DA, Milhorat TH. The blood brain barrier of the rat choroid plexus. Anat Rec 1975;181:779–790 - PubMed
-
- Netsky MG, Shuangshoti S. The Choroid Plexus in Health and Disease. Charlottesville, Va: University of Virginia Press;1975;249–264
-
- Igel HJ, Bolande RP. Humoral defense mechanisms in cryptococcosis: substances in normal human serum, saliva and CSF affecting the growth of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Infect Dis 1966;116:75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
