Distinct mechanisms of internalization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by members of the CEACAM receptor family involving Rac1- and Cdc42-dependent and -independent pathways
- PMID: 11847104
- PMCID: PMC125849
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.4.560
Distinct mechanisms of internalization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by members of the CEACAM receptor family involving Rac1- and Cdc42-dependent and -independent pathways
Abstract
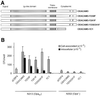
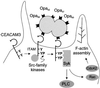
Opa adhesins of pathogenic Neisseria species target four members of the human carcinoembryonic antigen-related cellular adhesion molecule (CEACAM) family. CEACAM receptors mediate opsonization-independent phagocytosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human granulocytes and each receptor individually can mediate gonococcal invasion of epithelial cells. We show here that gonococcal internalization occurs by distinct mechanisms depending on the CEACAM receptor expressed. For the invasion of epithelial cell lines via CEACAM1 and CEACAM6, a pathogen-directed reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton is not required. In marked contrast, ligation of CEACAM3 triggers a dramatic but localized reorganization of the host cell surface leading to highly efficient engulfment of bacteria in a process regulated by the small GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42, but not Rho. Two tyrosine residues of a cytoplasmic immune receptor tyrosine-based activating motif of CEACAM3 are essential for the induction of phagocytic actin structures and subsequent gonococcal internalization. The granulocyte-specific CEACAM3 receptor has properties of a single chain phagocytic receptor and may thus contribute to innate immunity by the elimination of Neisseria and other CEACAM-binding pathogens that colonize human mucosal surfaces.
Figures
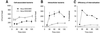





References
-
- Brummer J., Neumaier,M., Gopfert,C. and Wagener,C. (1995) Association of pp60c-src with biliary glycoprotein (CD66a), an adhesion molecule of the carcinoembryonic antigen family downregulated in colorectal carcinomas. Oncogene, 11, 1649–1655. - PubMed
-
- Cambier J.C. (1995) Antigen and Fc receptor signaling. The awesome power of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM). J. Immunol., 155, 3281–3285. - PubMed
-
- Caron E. and Hall,A. (1998) Identification of two distinct mechanisms of phagocytosis controlled by different Rho GTPases. Science, 282, 1717–1721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

