Role of the ubiquitin-selective CDC48(UFD1/NPL4 )chaperone (segregase) in ERAD of OLE1 and other substrates
- PMID: 11847109
- PMCID: PMC125867
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.4.615
Role of the ubiquitin-selective CDC48(UFD1/NPL4 )chaperone (segregase) in ERAD of OLE1 and other substrates
Abstract
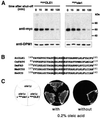
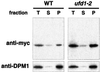
The OLE pathway of yeast regulates the abundance of the ER-bound enzyme Delta-9 fatty acid desaturase OLE1, thereby controlling unsaturated fatty acid pools and membrane fluidity. Previously, we showed that this pathway is exquisitely regulated by the ubiquitin/proteasome system. Activation of the pathway involves proteasomal processing of a membrane-bound transcription factor and the subsequent mobilization of the cleaved, ubiquitylated transcription factor from its partner molecule by CDC48(UFD1/NPL4), a ubiquitin-selective chaperone-like enzyme. Here we report that the OLE1 protein itself is naturally short-lived and is degraded by ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent ER-associated degradation (ERAD). We found that CDC48(UFD1/NPL4) plays a second role in the OLE pathway by mediating ERAD of OLE1. Intriguingly, other ERAD substrates also require CDC48(UFD1/NPL4) for degradation, indicating that this enzyme is a novel, constitutive component of the ERAD machinery. We propose that CDC48(UFD1/NPL4) functions as a segregase that liberates ubiquitylated proteins from non-modified partners.
Figures
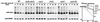


References
-
- Bays N.W., Gardner,R.G., Seelig,L.P., Joazeiro,C.A. and Hampton,R.Y. (2001) Hrd1p/Der3p is a membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase required for ER-associated degradation. Nature Cell Biol., 3, 24–29. - PubMed
-
- Biederer T., Volkwein,C. and Sommer,T. (1997) Role of Cue1p in ubiquitination and degradation at the ER surface. Science, 278, 1806–1809. - PubMed
-
- Chen P., Johnson,P., Sommer,T., Jentsch,S. and Hochstrasser,M. (1993) Multiple ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes participate in the in vivo degradation of the yeast MAT α2 repressor. Cell, 74, 357–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

