A heterochromatin protein 1 homologue in Caenorhabditis elegans acts in germline and vulval development
- PMID: 11850401
- PMCID: PMC1084015
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf051
A heterochromatin protein 1 homologue in Caenorhabditis elegans acts in germline and vulval development
Abstract
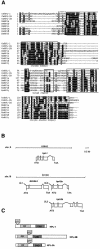
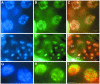
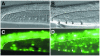
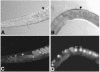
Proteins of the highly conserved heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) family have been found to function in the dynamic organization of nuclear architecture and in gene regulation throughout the eukaryotic kingdom. In addition to being key players in heterochromatin-mediated gene silencing, HP1 proteins may also contribute to the transcriptional repression of euchromatic genes via the recruitment to specific promoters. To investigate the role played by these different activities in specific developmental pathways, we identified HP1 homologues in the genome of Caenorhabditis elegans and used RNA-mediated interference to study their function. We show that one of the homologues, HPL-2, is required for the formation of a functional germline and for the development of the vulva by acting in an Rb-related pathway. We suggest that, by acting as repressors of gene expression, HP1 proteins may fulfil specific functions in both somatic and germline differentiation processes throughout development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The C. elegans HP1 homologue HPL-2 and the LIN-13 zinc finger protein form a complex implicated in vulval development.Dev Biol. 2006 Sep 15;297(2):308-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.04.474. Epub 2006 May 23. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16890929
-
Unique and redundant functions of C. elegans HP1 proteins in post-embryonic development.Dev Biol. 2006 Oct 1;298(1):176-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.039. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16905130
-
HPL-2/HP1 prevents inappropriate vulval induction in Caenorhabditis elegans by acting in both HYP7 and vulval precursor cells.Genetics. 2009 Feb;181(2):797-801. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.089276. Epub 2008 Dec 8. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19064713 Free PMC article.
-
Silence in the germ.Cell. 2002 Sep 20;110(6):661-4. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00967-4. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12297039 Review.
-
Pattern formation during C. elegans vulval induction.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2001;51:189-220. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(01)51006-6. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11236714 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-specific chromatin-binding patterns of Caenorhabditis elegans heterochromatin proteins HPL-1 and HPL-2 reveal differential roles in the regulation of gene expression.Genetics. 2023 Jul 6;224(3):iyad081. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad081. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37119802 Free PMC article.
-
The SynMuv genes of Caenorhabditis elegans in vulval development and beyond.Dev Biol. 2007 Jun 1;306(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.03.016. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17434473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analyses reveal protein and domain families that delineate stage-related development in the economically important parasitic nematodes, Ostertagia ostertagi and Cooperia oncophora.BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 22;14:118. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-118. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23432754 Free PMC article.
-
H3K9me1/2 methylation limits the lifespan of daf-2 mutants in C. elegans.Elife. 2022 Sep 20;11:e74812. doi: 10.7554/eLife.74812. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36125117 Free PMC article.
-
LIN-61, one of two Caenorhabditis elegans malignant-brain-tumor-repeat-containing proteins, acts with the DRM and NuRD-like protein complexes in vulval development but not in certain other biological processes.Genetics. 2007 May;176(1):255-71. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.069633. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17409073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ceol C.J. and Horvitz, R.H. (2001) dpl-1 DP and efl-1 E2F Act with lin-35 Rb to antagonise Ras signaling in C. elegans vulval development. Mol. Cell, 7, 461–473. - PubMed
-
- Eissenberg J.C. and Hartnett, T. (1993) A heat shock-activated cDNA rescues the recessive lethality of mutations in the heterochromatin-associated protein HP1 of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet., 240, 333–338. - PubMed
-
- Eissenberg J.C., James, T.C., Foster-Hartnett, D.M., Hartnett, T., Ngan, V. and Elgin, S.C. (1990) Mutation in a heterochromatin-specific chromosomal protein is associated with suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 9923–9927. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fay D.S. and Han, M. (2000) The synthetic multivulval genes of C. elegans: functional redundancy, Ras-antagonism, and cell fate determination. Genesis, 26, 279–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

