Mutual genetic antagonism involving GLI3 and dHAND prepatterns the vertebrate limb bud mesenchyme prior to SHH signaling
- PMID: 11850405
- PMCID: PMC155343
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.219202
Mutual genetic antagonism involving GLI3 and dHAND prepatterns the vertebrate limb bud mesenchyme prior to SHH signaling
Abstract
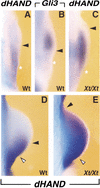
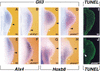
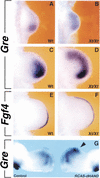
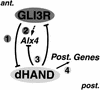
The bHLH transcription factor dHAND is required for establishment of SHH signaling by the limb bud organizer in posterior mesenchyme, a step crucial to development of vertebrate paired appendages. We show that the transcriptional repressor GLI3 restricts dHAND expression to posterior mesenchyme prior to activation of SHH signaling in mouse limb buds. dHAND, in turn, excludes anterior genes such as Gli3 and Alx4 from posterior mesenchyme. Furthermore, genetic interaction of GLI3 and dHAND directs establishment of the SHH/FGF signaling feedback loop by restricting the BMP antagonist GREMLIN posteriorly. These interactions polarize the nascent limb bud mesenchyme prior to SHH signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Buscher D, Bosse B, Heymer J, Ruther U. Evidence for genetic control of Sonic hedgehog by Gli3 in mouse limb development. Mech Dev. 1997;1997:175–182. - PubMed
-
- Charité J, de Graaff W, Shen S, Deschamps J. Ectopic expression of Hoxb-8 causes duplication of the ZPA in the forelimb and homeotic transformation of axial structures. Cell. 1994;78:589–601. - PubMed
-
- Charité J, McFadden DG, Olson EN. The bHLH transcription factor dHAND controls Sonic hedgehog expression and establishment of the zone of polarizing activity during limb development. Development. 2000;127:2461–2470. - PubMed
-
- Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Harris MP, Simandl BK, Li Y, Beachy PA, Fallon JF. Manifestation of the limb prepattern: Limb development in the absence of Sonic hedgehog function. Dev Biol. 2001;236:421–435. - PubMed
-
- Cohn MJ. Giving limbs a hand. Nature. 2000;406:953–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
