Knockout of Arabidopsis accelerated-cell-death11 encoding a sphingosine transfer protein causes activation of programmed cell death and defense
- PMID: 11850411
- PMCID: PMC155338
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.218202
Knockout of Arabidopsis accelerated-cell-death11 encoding a sphingosine transfer protein causes activation of programmed cell death and defense
Abstract
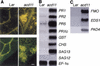
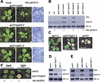
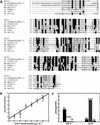
We describe the lethal, recessive accelerated-cell-death11 Arabidopsis mutant (acd11). Cell death in acd11 exhibits characteristics of animal apoptosis monitored by flow cytometry, and acd11 constitutively expresses defense-related genes that accompany the hypersensitive response normally triggered by avirulent pathogens. Global transcriptional changes during programmed cell death (PCD) and defense activation in acd11 were monitored by cDNA microarray hybridization. The PCD and defense pathways activated in acd11 are salicylic acid (SA) dependent, but do not require intact jasmonic acid or ethylene signaling pathways. Light is required for PCD execution in acd11, as application of an SA-analog to SA-deficient acd11 induced death in the light, but not in the dark. Epistatic analysis showed that the SA-dependent pathways require two regulators of SA-mediated resistance responses, PAD4 and EDS1. Furthermore, acd11 PR1 gene expression, but not cell death, depends on the SA signal tranducer NPR1, suggesting that the npr1-1 mutation uncouples resistance responses and cell death in acd11. The acd11 phenotype is caused by deletion of the ACD11 gene encoding a protein homologous to a mammalian glycolipid transfer protein (GLTP). In contrast to GLTP, ACD11 accelerates the transfer of sphingosine, but not of glycosphingolipids, between membranes in vitro.
Figures

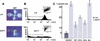
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
