Critical time-window for NO-cGMP-dependent long-term memory formation after one-trial appetitive conditioning
- PMID: 11850468
- PMCID: PMC6757551
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-04-01414.2002
Critical time-window for NO-cGMP-dependent long-term memory formation after one-trial appetitive conditioning
Abstract
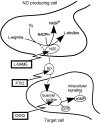
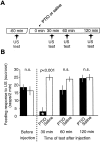
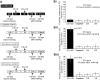
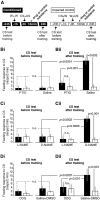
The nitric oxide (NO)-cGMP signaling pathway is implicated in an increasing number of experimental models of plasticity. Here, in a behavioral analysis using one-trial appetitive associative conditioning, we show that there is an obligatory requirement for this pathway in the formation of long-term memory (LTM). Moreover, we demonstrate that this requirement lasts for a critical period of approximately 5 hr after training. Specifically, we trained intact specimens of the snail Lymnaea stagnalis in a single conditioning trial using a conditioned stimulus, amyl-acetate, paired with a salient unconditioned stimulus, sucrose, for feeding. Long-term associative memory induced by a single associative trial was demonstrated at 24 hr and shown to last at least 14 d after training. Tests for LTM and its dependence on NO were performed routinely 24 hr after training. The critical period when NO was needed for memory formation was established by transiently depleting it from the animals at a series of time points after training by the injection of the NO-scavenger 2-phenyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide (PTIO). By blocking the activity of NO synthase and soluble guanylyl cyclase enzymes after training, we provided further evidence that LTM formation depends on an intact NO-cGMP pathway. An electrophysiological correlate of LTM was also blocked by PTIO, showing that the dependence of LTM on NO is amenable to analysis at the cellular level in vitro. This represents the first demonstration that associative memory formation after single-trial appetitive classical conditioning is dependent on an intact NO-cGMP signaling pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Critical role of nitric oxide-cGMP cascade in the formation of cAMP-dependent long-term memory.Learn Mem. 2006 Jan-Feb;13(1):35-44. doi: 10.1101/lm.130506. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16452652 Free PMC article.
-
A single time-window for protein synthesis-dependent long-term memory formation after one-trial appetitive conditioning.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Mar;21(5):1347-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03970.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15813944
-
Failure of delayed nonsynaptic neuronal plasticity underlies age-associated long-term associative memory impairment.BMC Neurosci. 2012 Aug 17;13:103. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-103. BMC Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22898271 Free PMC article.
-
The strength of aversive and appetitive associations and maladaptive behaviors.IUBMB Life. 2014 Aug;66(8):559-71. doi: 10.1002/iub.1310. Epub 2014 Sep 5. IUBMB Life. 2014. PMID: 25196552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the nitric oxide-soluble guanylyl cyclase pathway in obstructive airway diseases.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;29(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25043200 Review.
Cited by
-
Reconsolidation: does the past linger on?J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 25;26(43):10935-6; discussion 10936. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3694-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17068863 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, calmodulin, adenylyl cyclase, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II are required for late, but not early, long-term memory formation in the honeybee.Learn Mem. 2014 Apr 16;21(5):272-86. doi: 10.1101/lm.032037.113. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24741108 Free PMC article.
-
A homolog of the vertebrate pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is both necessary and instructive for the rapid formation of associative memory in an invertebrate.J Neurosci. 2010 Oct 13;30(41):13766-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2577-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20943917 Free PMC article.
-
Proactive and retroactive interference with associative memory consolidation in the snail Lymnaea is time and circuit dependent.Commun Biol. 2019 Jun 26;2:242. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0470-y. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31263786 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nitric oxide in the induction of the behavioral and cellular changes produced by a common aversive stimulus in Aplysia.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Mar 15;360:341-353. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30528940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike T, Yoshida M, Miyamoto Y, Sato K, Kohno M, Sasamoto K, Miyazaki K, Ueda S, Maeda H. Antagonistic action of imidazolineoxyl N-oxides against endothelium-derived relaxing factor/NO through a radical reaction. Biochemistry. 1993;32:827–832. - PubMed
-
- Alexander J, Jr, Audesirk TE, Audesirk GJ. One-trial reward learning in the snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurobiol. 1984;15:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Baratti CM, Kopf SR. A nitric oxide synthase inhibitor impairs memory storage in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1996;65:197–201. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin PR, Elliott CJH. Snail feeding oscillator: the central pattern generator and its control by modulatory interneurons. In: Jacklet J, editor. Neuronal and cellular oscillators. Dekker; New York: 1989. pp. 173–214.
-
- Benjamin PR, Rose RM. Central generation of bursting in the feeding system of the snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Exp Biol. 1979;80:93–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
