Fast Ca2+ signals at mouse inner hair cell synapse: a role for Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release
- PMID: 11850498
- PMCID: PMC2290124
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013171
Fast Ca2+ signals at mouse inner hair cell synapse: a role for Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release
Abstract
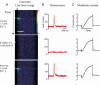
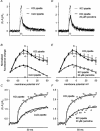
Inner hair cells of the mammalian cochlea translate acoustic stimuli into 'phase-locked' nerve impulses with frequencies of up to at least 1 kHz. Little is known about the intracellular Ca2+ signal that links transduction to the release of neurotransmitter at the afferent synapse. Here, we use confocal microscopy to provide evidence that Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) may contribute to the mechanism. Line scan images (2 ms repetition rate) of neonatal mouse inner hair cells filled with the fluorescent indicator FLUO-3, revealed a transient increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) during brief (5-50 ms) depolarizing commands under voltage clamp. The amplitude of the [Ca2+]i transient depended upon the Ca2+ concentration in the bathing medium in the range 0-1.3 mM. [Ca2+]i transients were confined to a region near the plasma membrane at the base of the cell in the vicinity of the afferent synapses. The change in [Ca2+]i appeared uniform throughout the entire basal sub-membrane space and we were unable to observe hotspots of activity. Both the amplitude and the rate of rise of the [Ca2+]i transient was reduced by external ryanodine (20 microM), an agent that blocks Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Intracellular Cs+, commonly used to record at presynaptic sites, produced a similar effect. We conclude that both ryanodine and intracellular Cs+ block CICR in inner hair cells. We discuss the contribution of CICR to the measured [Ca2+]i transient, the implications for synaptic transmission at the afferent synapse and the significance of its sensitivity to intracellular Cs+.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Presynaptic calcium stores modulate afferent release in vestibular hair cells.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 30;23(17):6894-903. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06894.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12890784 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium dependence of exocytosis and endocytosis at the cochlear inner hair cell afferent synapse.Neuron. 2001 Mar;29(3):681-90. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00243-4. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11301027
-
Phase-Locking Requires Efficient Ca2+ Extrusion at the Auditory Hair Cell Ribbon Synapse.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 24;41(8):1625-1635. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1324-18.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 14. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33446517 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated K(+) channels contributing to temporal precision at the inner hair cell-auditory afferent nerve fiber synapses in the mammalian cochlea.Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Jul;37(7):821-33. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0411-8. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24925343 Review.
-
Mechanisms underlying the temporal precision of sound coding at the inner hair cell ribbon synapse.J Physiol. 2006 Oct 1;576(Pt 1):55-62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.114835. Epub 2006 Aug 10. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16901948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent maturation of inner hair cell synaptic Ca2+ influx and auditory nerve spontaneous activity around hearing onset in mice.J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 26;33(26):10661-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1215-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23804089 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic calcium stores modulate afferent release in vestibular hair cells.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 30;23(17):6894-903. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06894.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12890784 Free PMC article.
-
Ryanodine Receptors Selectively Interact with L Type Calcium Channels in Mouse Taste Cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e68174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068174. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826376 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-Induced calcium release during action potential firing in developing inner hair cells.Biophys J. 2015 Mar 10;108(5):1003-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3489. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25762313 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium and calcium currents shape action potentials in immature mouse inner hair cells.J Physiol. 2003 Nov 1;552(Pt 3):743-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.043612. Epub 2003 Aug 22. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12937295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beutner D, Voets T, Neher E, Moser T. Calcium dependence of exocytosis and endocytosis at the cochlear inner hair cell afferent synapse. Neuron. 2001;29:681–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

