Nitric oxide inhibits capacitative Ca2+ entry and enhances endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake in bovine vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 11850503
- PMCID: PMC2290138
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013258
Nitric oxide inhibits capacitative Ca2+ entry and enhances endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake in bovine vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
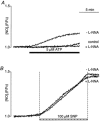
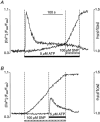
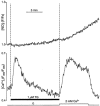
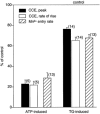
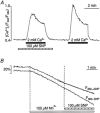
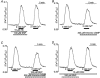
In vascular endothelial cells, elevation of cytosolic free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) causes activation of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and release of nitric oxide (NO). The goal of the study was to characterize the interplay between [Ca2+]i and NO production in this cell type. Simultaneous measurements of [Ca2+]i and intracellular NO concentration ([NO]i) in cultured bovine vascular endothelial cells (CPAE cell line) with the fluorescent indicators fura-2 and DAF-2, respectively, revealed that Ca2+ influx following agonist-induced intracellular Ca2+ store depletion (capacitative Ca2+ entry, CCE) represents the preferential Ca2+ source for the activation of the Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent endothelial NOS (eNOS). Exposure to the NO donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP) showed that high NO levels suppressed CCE and had an inhibitory effect on Ca2+ extrusion by the plasmalemmal Ca2+-ATPase. This inhibitory effect on CCE was mimicked by the membrane-permeant cGMP analogue 8-bromo-cGMP, but was reversed by the NO scavenger haemoglobin and prevented by the inhibitor of the NO-sensitive guanylate cyclase ODQ. Brief exposure to SNP reduced the peak of ATP-induced Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and accelerated Ca2+ reuptake into the ER. Prolonged incubation with SNP resulted in enhanced Ca2+ loading of the ER, as revealed by direct measurements of store content with the ER-entrapped low-affinity Ca2+ indicator mag-fura-2. The results suggest that in vascular endothelial cells, NO synthesis is under autoregulatory control that involves NO-dependent [Ca2+]i regulation. Via cGMP-dependent inhibition of CCE and acceleration of Ca2+ sequestration into the ER, NO can lower [Ca2+]i and therefore exert an autoregulatory negative feedback on its own Ca2+-dependent synthesis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Capacitative Ca2+ entry is graded with degree of intracellular Ca2+ store depletion in bovine vascular endothelial cells.J Physiol. 2000 Mar 15;523 Pt 3(Pt 3):549-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-3-00549.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10718737 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide induces transient Ca2+ changes in endothelial cells independent of cGMP.J Cell Physiol. 1997 Sep;172(3):296-305. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199709)172:3<296::AID-JCP3>3.0.CO;2-J. J Cell Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9284949
-
The effect of oxidative stress on Ca2+ release and capacitative Ca2+ entry in vascular endothelial cells.Cell Calcium. 2008 Apr;43(4):405-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.07.005. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Cell Calcium. 2008. PMID: 17767954
-
Possible regulation of capacitative Ca2+ entry into colonic epithelial cells by NO and cGMP.Cell Calcium. 1995 Apr;17(4):250-62. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(95)90071-3. Cell Calcium. 1995. PMID: 7545090
-
From nitric oxide to endothelial cytosolic Ca2+: a negative feedback control.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Jun;24(6):263-6. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00122-6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12823948 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular calcium signals and control of cell proliferation: how many mechanisms?J Cell Mol Med. 2004 Apr-Jun;8(2):161-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00271.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15256064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cGMP reduces the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ loading in airway smooth muscle cells: a putative mechanism in the regulation of Ca2+ by cGMP.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2012 Mar;32(6):375-82. doi: 10.1007/s10974-011-9266-5. Epub 2011 Oct 15. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2012. PMID: 21997642
-
Shear stress-induced NO production is dependent on ATP autocrine signaling and capacitative calcium entry.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2014 Dec 1;7(4):510-520. doi: 10.1007/s12195-014-0351-x. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2014. PMID: 25386222 Free PMC article.
-
The machinery of healthy vasoconstriction: an overview.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03103-6. Online ahead of print. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 40640430 Review.
-
Lipid Emulsions Inhibit Labetalol-Induced Vasodilation in the Isolated Rat Aorta.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 30;25(13):7243. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137243. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berkels R, Dachs C, Roesen R, Klaus W. Simultaneous measurement of intracellular Ca2+ and nitric oxide: A new method. Cell Calcium. 2000a;25:281–286. - PubMed
-
- Berkels R, Suerhoff S, Roesen R, Klaus W. Nitric oxide causes a cGMP-independent intracellular calcium rise in porcine endothelial cells - a paradox? Microvascular Research. 2000b;59:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Bischof G, Serwold TS, Machen TE. Does nitric oxide regulate capacitative Ca2+ influx in HEK 293 cells? Cell Calcium. 1997;21:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Blatter LA, Wier WG. Nitric oxide decreases [Ca2+]i in vascular smooth muscle by inhibition of the calcium current. Cell Calcium. 1994;15:122–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

