Order and disorder: the role of extracellular matrix in epithelial cancer
- PMID: 11852996
- PMCID: PMC2933209
- DOI: 10.1081/cnv-120000374
Order and disorder: the role of extracellular matrix in epithelial cancer
Figures

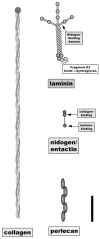
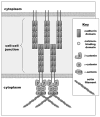
References
-
- Bissell MJ, Hall HG, Parry G. How Does Extracellular Matrix Direct Gene Expression? J Theor Biol. 1982;99(1):31–68. - PubMed
-
- Howe A, Aplin AE, Alahari SK, Juliano RL. Integrin Signaling and Cell Growth Control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10(2):220–231. - PubMed
-
- De Archangelis A, Georges-Labouesse E. Integrin and ECM Functions: Roles in Vertebrate Development. Trends Genet. 2000;16(9):389–395. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson E, Fässler R. Insights into Extracellular Matrix Functions from Mutant Mouse Models. Exp Cell Res. 2000;261(1):52–68. - PubMed
-
- Tsai LH. Stuck on the ECM. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8(7):292–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
