Human gingival CD14(+) fibroblasts primed with gamma interferon increase production of interleukin-8 in response to lipopolysaccharide through up-regulation of membrane CD14 and MyD88 mRNA expression
- PMID: 11854210
- PMCID: PMC127773
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1272-1278.2002
Human gingival CD14(+) fibroblasts primed with gamma interferon increase production of interleukin-8 in response to lipopolysaccharide through up-regulation of membrane CD14 and MyD88 mRNA expression
Abstract
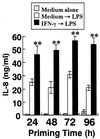
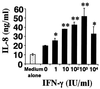
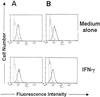
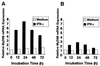
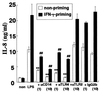
Gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-primed human gingival fibroblasts (HGF) have been shown to produce higher levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8) upon stimulation with bacterial products and inflammatory cytokines than nonprimed controls. In this study, we examined whether priming of HGF with IFN-gamma up-regulates IL-8 production by the cells in response to purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The priming effect of IFN-gamma was clearly observed in the high-CD14-expressing (CD14(high)) HGF but not in the low-CD14-expressing (CD14(low)) HGF. The CD14(high) HGF were most effectively primed with IFN-gamma (1,000 IU/ml) for 72 h. To elucidate the mechanism of the priming effects of IFN-gamma for the LPS response by HGF, we examined whether IFN-gamma regulated expression of CD14, Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), TLR4, MD-2, and MyD88, all of which are molecules suggested to be associated with LPS signaling. In CD14(high) HGF, IFN-gamma markedly up-regulated CD14 and MyD88 but not TLR4 protein and MD-2 mRNA expression, while in CD14(low) HGF, IFN-gamma slightly increased MyD88 and scarcely affected CD14, TLR4 protein, and MD-2 mRNA levels. LPS-induced IL-8 production by IFN-gamma-primed CD14(high) HGF was significantly inhibited by monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against CD14 and TLR4, but not by an anti-TLR2 MAb. These findings suggested that IFN-gamma primed CD14(high) HGF to enhance production of IL-8 in response to LPS through augmentation of the CD14-TLR system, where the presence of membrane CD14 was indispensable for the response of HGF to LPS.
Figures
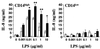

Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma in inducing interleukin-8 production in human monocytic THP-1 cells is accompanied by up-regulation of CD14, Toll-like receptor 4, MD-2 and MyD88 expression.J Endotoxin Res. 2003;9(3):145-53. doi: 10.1179/096805103125001540. J Endotoxin Res. 2003. PMID: 12831455
-
Gamma-interferon enhances expression of CD14/MyD88 and subsequent responsiveness to lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human gingival fibroblasts.J Periodontal Res. 2004 Oct;39(5):333-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2004.00749.x. J Periodontal Res. 2004. PMID: 15324355
-
Priming of human oral epithelial cells by interferon-gamma to secrete cytokines in response to lipopolysaccharides, lipoteichoic acids and peptidoglycans.J Med Microbiol. 2002 Aug;51(8):626-634. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-8-626. J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12171292
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide signaling in gingival fibroblasts-CD14 and Toll-like receptors.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13(2):132-42. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300204. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002. PMID: 12097356 Review.
-
Enhancement of endotoxin activity by muramyldipeptide.J Endotoxin Res. 2002;8(5):337-42. doi: 10.1179/096805102125000669. J Endotoxin Res. 2002. PMID: 12537692 Review.
Cited by
-
Alendronate augments lipid A‑induced IL‑1β release by ASC‑deficient RAW264 cells via AP‑1 activation.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Oct 26;26(6):577. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12276. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 38023354 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of Candida albicans by gingival fibroblasts: The role of TLR2, TLR4/CD14, and MyD88.Cytokine. 2018 Jun;106:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29128406 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-anchored CD14 is important for induction of interleukin-8 by lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan in uroepithelial cells.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 Sep;11(5):969-76. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.5.969-976.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15358661 Free PMC article.
-
Evodiae fructus Extract Inhibits Interleukin-1β-Induced MMP-1, MMP-3, and Inflammatory Cytokine Expression by Suppressing the Activation of MAPK and STAT-3 in Human Gingival Fibroblasts In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 31;2021:5858393. doi: 10.1155/2021/5858393. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34504537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi, O., T. Kawai, K. Takeda, M. Matsumoto, H. Tsutsui, M. Sakagami, K. Nakanishi, and S. Akira. 1998. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity 9:143-150. - PubMed
-
- Aderem, A., and R. J. Ulevitch. 2000. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406:782-787. - PubMed
-
- Akashi, S., H. Ogata, F. Kirikae, T. Kirikae, K. Kawasaki, M. Nishijima, R. Shimazu, Y. Nagai, K. Fukudome, M. Kimoto, and K. Miyake. 2000. Regulatory roles for CD14 and phosphatidylinositol in the signaling via Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 268:172-177. - PubMed
-
- Akashi, S., R. Shimazu, H. Ogata, Y. Nagai, K. Takeda, M. Kimoto, and K. Miyake. 2000. Cell surface expression and lipopolysaccharide signaling via the Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2 complex on mouse peritoneal macrophages. J. Immunol. 164:3471-3475. - PubMed
-
- Bovolenta, C., P. H. Driggers, M. S. Marks, J. A. Medin, A. D. Politis, S. N. Vogel, D. E. Levy, K. Sakaguchi, E. Appella, J. E. Coligan, and K. Ozato. 1994. Molecular interactions between interferon consensus sequence binding protein and members of the interferon regulatory factor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:5046-5050. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

