Cloned Shiga toxin 2 B subunit induces apoptosis in Ramos Burkitt's lymphoma B cells
- PMID: 11854211
- PMCID: PMC127801
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1279-1286.2002
Cloned Shiga toxin 2 B subunit induces apoptosis in Ramos Burkitt's lymphoma B cells
Retraction in
-
Cloned Shiga toxin 2 B subunit induces apoptosis in Ramos Burkitt's lymphoma B cells.Infect Immun. 2003 Aug;71(8):4828. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4828.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12894765 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
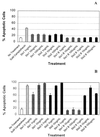
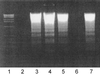
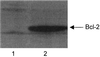
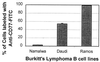
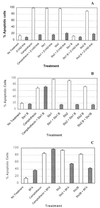
The Shiga toxins (Stx1 and Stx2), produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli, consist of one A subunit and five B subunits. The Stx1 and Stx2 B subunits form a pentameric structure that binds to globotriaosylceramide (Gb3-Cer) receptors on eukaryotic cells and promotes endocytosis. The A subunit then inhibits protein biosynthesis, which triggers apoptosis in the affected cell. In addition to its Gb3-Cer binding activity, the data in the following report demonstrate that the Stx2 B pentamer induces apoptosis in Ramos Burkitt's lymphoma B cells independently of A subunit activity. Apoptosis was not observed in A subunit-free preparations of the Stx1 B pentamer which competitively inhibited Stx2 B pentamer-mediated apoptosis. The pancaspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-fmk, prevented apoptosis in Ramos cells exposed to the Stx2 B subunit, Stx1 or Stx2. Brefeldin A, an inhibitor of the Golgi transport system, also prevented Stx2 B subunit-mediated apoptosis. These observations suggest that the Stx2 B subunit must be internalized, via Gb3-Cer receptors, to induce Ramos cell apoptosis. Moreover, unlike the two holotoxins, Stx2 B subunit-mediated apoptosis does not involve inhibition of protein biosynthesis. This study provides further insight into the pathogenic potential of this family of potent bacterial exotoxins.
Figures


References
-
- Acheson, D. W., M. Jacewicz, A. V. Kane, A. Donohue-Rolfe, and G. T. Keusch. 1993. One-step high-yield affinity purification of shiga-like toxin II variants and quantitation using enzyme linked immunosorbent assays. Microb. Pathog. 14:57-66. - PubMed
-
- Arab, S., M. Murakami, P. Dirks, B. Boyd, S. L. Hubbard, C. A. Lingwood, and J. T. Rutka. 1998. Verotoxins inhibit the growth of and induce apoptosis in human astrocytoma cells. J. Neurooncol. 40:137-150. - PubMed
-
- Brown, J. E., M. A. Ussery, S. H. Leppla, and S. W. Rothman. 1980. Inhibition of protein synthesis by Shiga toxin: activation of the toxin and inhibition of peptide elongation. FEBS Lett. 117:84-88. - PubMed
-
- Chinnaiyan, A. M., K. O'Rourke, M. Tewari, and V. M. Dixit. 1995. FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81:505-512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

