Genetic models: clues for understanding the pathogenesis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 11854315
- PMCID: PMC150884
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15094
Genetic models: clues for understanding the pathogenesis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
Figures
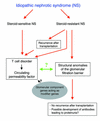
Comment on
-
Extrarenal effects on the pathogenesis and relapse of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in Buffalo/Mna rats.J Clin Invest. 2002 Feb;109(4):491-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI12858. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 11854321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chadban SJ. Glomerulonephritis recurrence in the renal graft. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:394–402. - PubMed
-
- Dantal J, et al. Antihuman immunoglobulin affinity immunoadsorption strongly decreases proteinuria in patients with relapsing nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:1709–1715. - PubMed
-
- Fuchshuber A, et al. Clinical and genetic evaluation of familial steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome in childhood. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:374–378. - PubMed
-
- Tejani A, Stablein DH. Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis posttransplantation: a special report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992;2:S258–S263. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan JM, et al. Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet. 2000;24:251–256. - PubMed

