Virus-induced interferon alpha production by a dendritic cell subset in the absence of feedback signaling in vivo
- PMID: 11854363
- PMCID: PMC2193622
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20011666
Virus-induced interferon alpha production by a dendritic cell subset in the absence of feedback signaling in vivo
Abstract
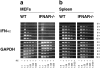
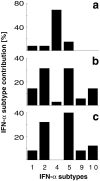
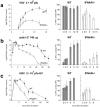
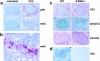
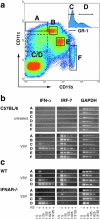
An effective type I interferon (IFN-alpha/beta) response is critical for the control of many viral infections. Here we show that in vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-infected mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) the production of IFN-alpha is dependent on type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) triggering, whereas in infected mice early IFN-alpha production is IFNAR independent. In VSV-infected mice type I IFN is produced by few cells located in the marginal zone of the spleen. Unlike other dendritic cell (DC) subsets, FACS((R))-sorted CD11c(int)CD11b(-)GR-1(+) DCs show high IFN-alpha expression, irrespective of whether they were isolated from VSV-infected IFNAR-competent or -deficient mice. Thus, VSV preferentially activates a specialized DC subset presumably located in the marginal zone to produce high-level IFN-alpha largely independent of IFNAR feedback signaling.
Figures


Comment in
-
Whence interferon? Variety in the production of interferon in response to viral infection.J Exp Med. 2002 Feb 18;195(4):F15-8. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020075. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 11854366 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Isaacs, A., and J. Lindenmann. 1957. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 147:258–267. - PubMed
-
- Gresser, I., M.G. Tovey, C. Maury, and M.T. Bandu. 1976. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. II. Studies with herpes simplex, Moloney sarcoma, vesicular stomatitis, Newcastle disease, and influenza viruses. J. Exp. Med. 144:1316–1323. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muller, U., U. Steinhoff, L.F. Reis, S. Hemmi, J. Pavlovic, R.M. Zinkernagel, and M. Aguet. 1994. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 264:1918–1921. - PubMed
-
- Le Bon, A., G. Schiavoni, G. D'Agostino, I. Gresser, F. Belardelli, and D.F. Tough. 2001. Type I interferons potently enhance humoral immunity and can promote isotype switching by stimulating dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity. 14:461–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

