The Drosophila nuclear lamina protein YA binds to DNA and histone H2B with four domains
- PMID: 11854412
- PMCID: PMC65649
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.01-07-0336
The Drosophila nuclear lamina protein YA binds to DNA and histone H2B with four domains
Abstract
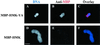
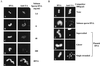
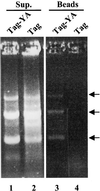
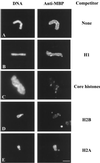
Dramatic changes occur in nuclear organization and function during the critical developmental transition from meiosis to mitosis. The Drosophila nuclear lamina protein YA binds to chromatin and is uniquely required for this transition. In this study, we dissected YA's binding to chromatin. We found that YA can bind to chromatin directly and specifically. It binds to DNA but not RNA, with a preference for double-stranded DNA (linear or supercoiled) over single-stranded DNA. It also binds to histone H2B. YA's binding to DNA and histone H2B is mediated by four domains distributed along the length of the YA molecule. A model for YA function at the end of Drosophila female meiosis is proposed.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interaction of the essential Drosophila nuclear protein YA with P0/AP3 in the cytoplasm and in vitro: implications for developmental regulation of YA's subcellular location.Dev Biol. 2002 Apr 15;244(2):429-41. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2002.0601. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11944949
-
The developmentally regulated Drosophila embryonic nuclear lamina protein 'Young Arrest' (fs(1)Ya) is capable of associating with chromatin.J Cell Sci. 1997 Mar;110 ( Pt 5):643-51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110.5.643. J Cell Sci. 1997. PMID: 9092946
-
YA is needed for proper nuclear organization to transition between meiosis and mitosis in Drosophila.BMC Dev Biol. 2009 Jul 23;9:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-43. BMC Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19627584 Free PMC article.
-
[Setting the stage for mitosis: kinase regulation of prophase].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004 Jun;49(8):1183-94. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004. PMID: 15209214 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
The right dose for every sex.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0089-x. Epub 2006 Nov 24. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17124606 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of maternal transcript destabilization during egg activation in Drosophila.Genetics. 2003 Jul;164(3):989-1001. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.3.989. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 12871909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berman CL. The Role of YA Protein in Drosophila Female Meiosis [M.S. Thesis]. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University; 2000.
-
- Blanar MA, Rutter WJ. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992;256:1014–1018. - PubMed
-
- Bulger M, Kadonaga JT. Biochemical reconstitution of chromatin with physiological nucleosome spacing. Meth Molec Genet. 1994;5:241–262.
-
- Callaini G, Riparbelli MG. Fertilization in Drosophila melanogaster: centrosome inheritance and organization of the first mitotic spindle. Dev Biol. 1996;176:199–208. - PubMed
-
- Cameron LA, Poccia DL. In vitro development of the sea urchin male pronucleus. Dev Biol. 1994;162:568–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

