Feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and lipoic acid to old rats significantly improves metabolic function while decreasing oxidative stress
- PMID: 11854487
- PMCID: PMC122286
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261708898
Feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and lipoic acid to old rats significantly improves metabolic function while decreasing oxidative stress
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002 May 14;99(10):7184
Abstract
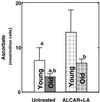
Mitochondrial-supported bioenergetics decline and oxidative stress increases during aging. To address whether the dietary addition of acetyl-l-carnitine [ALCAR, 1.5% (wt/vol) in the drinking water] and/or (R)-alpha-lipoic acid [LA, 0.5% (wt/wt) in the chow] improved these endpoints, young (2-4 mo) and old (24-28 mo) F344 rats were supplemented for up to 1 mo before death and hepatocyte isolation. ALCAR+LA partially reversed the age-related decline in average mitochondrial membrane potential and significantly increased (P = 0.02) hepatocellular O(2) consumption, indicating that mitochondrial-supported cellular metabolism was markedly improved by this feeding regimen. ALCAR+LA also increased ambulatory activity in both young and old rats; moreover, the improvement was significantly greater (P = 0.03) in old versus young animals and also greater when compared with old rats fed ALCAR or LA alone. To determine whether ALCAR+LA also affected indices of oxidative stress, ascorbic acid and markers of lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde) were monitored. The hepatocellular ascorbate level markedly declined with age (P = 0.003) but was restored to the level seen in young rats when ALCAR+LA was given. The level of malondialdehyde, which was significantly higher (P = 0.0001) in old versus young rats, also declined after ALCAR+LA supplementation and was not significantly different from that of young unsupplemented rats. Feeding ALCAR in combination with LA increased metabolism and lowered oxidative stress more than either compound alone.
Figures



References
-
- Miquel J, Economos A C, Fleming J, Johnson J E. Exp Gerontol. 1980;15:575–591. - PubMed
-
- Harmon D. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1972;20:145–147. - PubMed
-
- Sohal R S, Sohal B H. Mech Ageing Dev. 1991;57:187–202. - PubMed
-
- Sohal R S, Sohal B H, Orr W C. Free Radical Biol Med. 1995;19:499–504. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Campo R, Lopez-Torres M, Cadenas S, Rojas C, Barja G. J Comp Physiol. 1998;168:149–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

