Targeting endothelium and its dynamic caveolae for tissue-specific transcytosis in vivo: a pathway to overcome cell barriers to drug and gene delivery
- PMID: 11854497
- PMCID: PMC122308
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251662398
Targeting endothelium and its dynamic caveolae for tissue-specific transcytosis in vivo: a pathway to overcome cell barriers to drug and gene delivery
Abstract
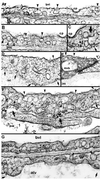
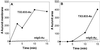
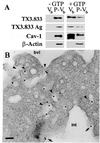
Site-directed pharmacodelivery is a desirable but elusive goal. Endothelium and epithelium create formidable barriers to endogenous molecules as well as targeted therapies in vivo. Caveolae provide a possible, yet unproven, transcellular pathway to overcome such barriers. By using an antibody- and subfractionation-based strategy, we generated a monoclonal antibody specific for lung caveolae (TX3.833) that targets rat lungs after i.v. injection (up to 89% of dose in 30 min). Unlike control antibodies (nonbinding or to lipid rafts), TX3.833 targets lung caveolae that bud to form free vesicles for selective and quantal transendothelial transport to underlying tissue cells in vivo. Rapid sequential transcytosis can occur to the alveolar air space via epithelial caveolae. Conjugation to TX3.833 increases drug delivery to the lung up to 172-fold and achieves rapid, localized bioefficacy. We conclude that: (i) molecular heterogeneity of the endothelium and its caveolae permits vascular targeting to achieve theoretical expectations of tissue-specific delivery and bioefficacy; (ii) caveolae can mediate selective transcytosis in vivo; and (iii) targeting caveolae may provide a tissue-specific pathway for overcoming key cell barriers to many drug and gene therapies in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Jain R K. Nat Med. 1998;4:655–657. - PubMed
-
- Miller N, Vile R. FASEB J. 1995;9:190–199. - PubMed
-
- Thrush G R, Lark L A, Clinchy B C, Vitetta E S. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:49–71. - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson E. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 1987;1:87–198.
-
- Dvorak H F, Nagy J A, Dvorak A M. Cancer Cells. 1991;3:77–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

