p56Lck anchors CD4 to distinct microdomains on microvilli
- PMID: 11854499
- PMCID: PMC122310
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.042689099
p56Lck anchors CD4 to distinct microdomains on microvilli
Abstract
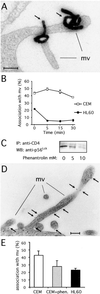
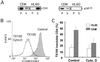
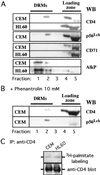
Cell-surface microvilli play a central role in adhesion, fusion, and signaling processes. Some adhesion and signaling receptors segregate on microvilli but the determinants of this localization remain mostly unknown. In this study, we considered CD4, a receptor involved in immune response and HIV infection, and p56(Lck), a CD4-associated tyrosine kinase. Analysis of CD4 trafficking reveals that p56(Lck) binds tightly to CD4 independently of its activation state and inhibits CD4 internalization. Electron microscopy analysis established that p56(Lck) mediates CD4 association with microvilli whereas biochemical data indicate that p56(Lck) expression renders CD4 insoluble by the nonionic detergent Triton X-100. In addition, cytoskeleton-disrupting agent increased CD4 solubility, suggesting the involvement of cytoskeletal elements in CD4 anchoring to microvilli. This concept was supported further by the observation that the lateral mobility of CD4 within the plasma membrane was decreased in cells expressing p56(Lck). Finally, isolation of detergent-resistant membranes revealed that the complex CD4-p56(Lck) is enriched within these domains as opposed to conditions in which CD4 does not interact with p56(Lck). In conclusion, our results show that p56(Lck) targets CD4 to specialized lipid microdomains preferentially localized on microvilli. This localization, which prevents CD4 internalization, might facilitate CD4-mediated adhesion processes and could correspond to the signaling site of the receptor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HIV-1 Nef plays an essential role in two independent processes in CD4 down-regulation: dissociation of the CD4-p56(lck) complex and targeting of CD4 to lysosomes.Virology. 1999 Apr 25;257(1):208-19. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9642. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10208934
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase participates in p56(lck)/CD4-dependent down-regulation of LFA-1-mediated T cell adhesion.J Immunol. 1996 Dec 1;157(11):4844-54. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8943387
-
Dynamic reorganization of chemokine receptors, cholesterol, lipid rafts, and adhesion molecules to sites of CD4 engagement.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Apr 1;304(2):559-69. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.11.022. Epub 2004 Dec 23. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15748900
-
Sequestration of p56(lck) by gp120, a model for TCR desensitization.J Immunol. 1997 Mar 1;158(5):2017-24. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9036944
-
p56lck, LFA-1 and PI3K but not SHP-2 interact with GM1- or GM3-enriched microdomains in a CD4-p56lck association-dependent manner.Biochem J. 2007 Mar 15;402(3):471-81. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061061. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17123354 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The transmembrane domains of L-selectin and CD44 regulate receptor cell surface positioning and leukocyte adhesion under flow.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 30;285(18):13490-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102640. Epub 2010 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20212041 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cholesterol in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein-mediated fusion with host cells.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11584-95. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11584-11595.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388719 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of T-cell receptor signalling by membrane microdomains.Immunology. 2004 Dec;113(4):413-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01998.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15554919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobility of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) receptor CD4 and coreceptor CCR5 in living cells: implications for HIV fusion and entry events.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9573-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9573-9578.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308751 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of CD4 and CCR5 in living cells.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(8):4985-91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4985-4991.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12663805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiss A, Littman D R. Cell. 1994;76:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Foti M, Lew D P, Carpentier J L, Krause K H. J Lab Clin Med. 1995;126:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Klatzmann D, Champagne E, Chamaret S, Gruest J, Guetard D, Hercend T, Gluckman J C, Montagnier L. Nature (London) 1984;312:767–768. - PubMed
-
- Veillette A, Bookman M A, Horak E M, Bolen J B. Cell. 1988;55:301–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

