Memory loss in old rats is associated with brain mitochondrial decay and RNA/DNA oxidation: partial reversal by feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and/or R-alpha -lipoic acid
- PMID: 11854529
- PMCID: PMC122369
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261709299
Memory loss in old rats is associated with brain mitochondrial decay and RNA/DNA oxidation: partial reversal by feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and/or R-alpha -lipoic acid
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002 May 14;99(10):7184-5
Abstract
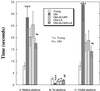
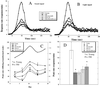
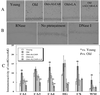
Accumulation of oxidative damage to mitochondria, protein, and nucleic acid in the brain may lead to neuronal and cognitive dysfunction. The effects on cognitive function, brain mitochondrial structure, and biomarkers of oxidative damage were studied after feeding old rats two mitochondrial metabolites, acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) [0.5% or 0.2% (wt/vol) in drinking water], and/or R-alpha-lipoic acid (LA) [0.2% or 0.1% (wt/wt) in diet]. Spatial memory was assessed by using the Morris water maze; temporal memory was tested by using the peak procedure (a time-discrimination procedure). Dietary supplementation with ALCAR and/or LA improved memory, the combination being the most effective for two different tests of spatial memory (P < 0.05; P < 0.01) and for temporal memory (P < 0.05). Immunohistochemical analysis showed that oxidative damage to nucleic acids (8-hydroxyguanosine and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine) increased with age in the hippocampus, a region important for memory. Oxidative damage to nucleic acids occurred predominantly in RNA. Dietary administration of ALCAR and/or LA significantly reduced the extent of oxidized RNA, the combination being the most effective. Electron microscopic studies in the hippocampus showed that ALCAR and/or LA reversed age-associated mitochondrial structural decay. These results suggest that feeding ALCAR and LA to old rats improves performance on memory tasks by lowering oxidative damage and improving mitochondrial function.
Figures
References
-
- Grady C L, McIntosh A R, Horwitz B, Maisog J M, Ungerleider L G, Mentis M J, Pietrini P, Schapiro M B, Haxby J V. Science. 1995;269:218–221. - PubMed
-
- Wallace J E, Krauter E E, Campbell B A. J Gerontol. 1980;35:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Rahner-Welsch S, Frolich L, Stoll S, Hoyer S. Neurosci Lett. 1995;194:121–123. - PubMed
-
- Head E, Mehta R, Hartley J, Kameka M, Cummings B J, Cotman C W, Ruehl W W, Milgram N W. Behav Neurosci. 1995;109:851–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

