Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of Sulindac on Human gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 11854904
- PMCID: PMC4695597
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.796
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of Sulindac on Human gastric cancer cells
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effects of sulindac in inducing growth inhibition and apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells in comparison with human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells.
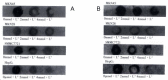
Methods: The human gastric cancer cell lines MKN45 and MKN28 and human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines HepG(2) and SMMC7721 were used for the study. Anti-proliferative effect was measured by MTT assay, and apoptosis was determined by Hoechst-33258 staining, electronography and DNA fragmentation. The protein of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Bcl-2 were detected by Western dot blotting.
Results: Sulindac could initiate growth inhibition and apoptosis of MKN45, MKN28, HepG(2) and SMMC7721 cells in a dose-and time-dependent manner. Growth inhibitory activity and apoptosis were more sensitive in HepG(2) cells than in SMMC7721 cells, MKN45 and MKN28 cells. After 24 hours incubation with sulindac at 2mmol x L(-1) and 4mmol x L(-1), the level of COX-2 and Bcl-2 protein were lowered in MKN45, SMMC7721 and HepG(2) cells but not in MKN28 cells.
Conclusion: Sulindac could inhibit the growth of gastric cancer cells and HCC cells effectively in vitro by apoptosis induction, which was associated with regression of COX-2 and Bcl-2 expression. The growth inhibition and apoptosis of HCC cells were greater than that of human gastric cancer cells. The different effects of apoptosis in gastric cancer cells may be related to the differentiation of the cells.
Figures



References
-
- Binder HY. Prevention of colorectal cancer: tumor progression chemop re vention, and cox-2 inhibition. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:267–272. - PubMed
-
- Yuan CJ, Mandal AK, Zhang Z, Mukherjee AB. Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression: novel effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1084–1091. - PubMed
-
- Zhu GH, Wong BC, Ching CK, Lai KC, Lam SK. Differential apoptosis by indomethacin in gastric epithelial cells through the constitutive expression of wild-type p53 and/or up-regulation of c-myc. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Stoner GD, Budd GT, Ganapathi R, DeYoung B, Kresty LA, Nitert M, Fryer B, Church JM, Provencher K, Pamukcu R, et al. Sulindac sulfone induced regression of rectal polyps in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;470:45–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

