Expression of lipopolysaccharide binding protein and its receptor CD14 in experimental alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 11854912
- PMCID: PMC4695605
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.836
Expression of lipopolysaccharide binding protein and its receptor CD14 in experimental alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the relationship between the expression of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) binding protein (LBP) and CD14 mRNA and the severity of liver injury in alcohol-fed rats.
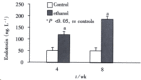
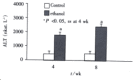
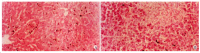
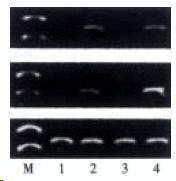
Methods: Twenty Wistar rats were divided into two groups:ethanol-fed group (group E) and control group (group C). Group E was fed with ethanol(5-12 g x kg(-1) x d(-1)) and group C received dextrose instead of ethanol. Rats of the two groups were sacrificed at 4 weeks and 8 weeks. Levels of endotoxin and alanine transaminase (ALT) in blood were measured, and liver pathology was observed under light and electronic microscopy. Expressions of LBP and CD14 mRNA in liver tissues were determined by RT-PCR analysis.
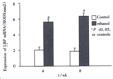
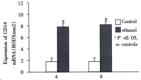
Results: Plasma endotoxin levels were increased more significantly in group E(129+/-21) ng x L(-1) and (187+/-35) ng x L(-1) at 4 and 8 wk than in control rats(48+/-9) ng x L(-1) and (53+/-11) ng x L(-1), respectively (P<0.05). Mean values of plasma ALT levels were (1867+/-250) nkat x L(-1) and (2450+/-367) nkat x L(-1) in Group E. The values were increased more dramatically in ethanol-fed rats than in Group C after 4 and 8 weeks. In liver section from ethanol-fed rats, there were marked pathological changes (steatosis, cell infiltration and necrosis). In ethanol-fed rats, ethanol administration led to a significant increase in LBP and CD14 mRNA levels compared with the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Ethanol administration led to a significant increase in endotoxin levels in serum and LBP and CD14 mRNA expressions in liver tissues. The increase of LBP and CD14 mRNA expression might wake the liver more sensitive to endotoxin and liver injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of endotoxin receptor CD14 protein in Kupffer cells and its role in alcohol-induced liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):622-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.622. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632533 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of lipopolysaccharide binding protein and lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 in experimental alcoholic liver disease].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2002 Jun;10(3):207-10. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12113681 Chinese.
-
CD14 and lipopolysaccharide binding protein expression in a rat model of alcoholic liver disease.Am J Pathol. 1998 Mar;152(3):841-9. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9502426 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 gene expression after thermal injury and its potential mechanism(s).J Trauma. 2002 Nov;53(5):957-67. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200211000-00024. J Trauma. 2002. PMID: 12435950
-
Relation of endotoxin, endotoxin binding proteins and macrophages to severe alcoholic liver injury and multiple organ failure.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Nov;29(11 Suppl):172S-179S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000189278.30237.e9. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16344605 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):562-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.562. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632519 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of alcoholic liver disease in the baboon (Papio hamadryas) and human liver.Am J Pathol. 2003 Dec;163(6):2303-17. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63587-0. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14633604 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor kB activity in patients with acute severe cholangitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Apr;8(2):346-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i2.346. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 11925622 Free PMC article.
-
Betaine inhibits toll-like receptor 4 expression in rats with ethanol-induced liver injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Feb 21;16(7):897-903. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i7.897. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20143470 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of endotoxin receptor CD14 protein in Kupffer cells and its role in alcohol-induced liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):622-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.622. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujimoto M, Uemura M, Nakatani Y, Tsujita S, Hoppo K, Tamagawa T, Kitano H, Kikukawa M, Ann T, Ishii Y, et al. Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: relation to severity of liver disturbance. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:48S–54S. - PubMed
-
- Zhang SC, Dai Q, Wang JY, He BM, Zhou K. Gut derived endotoxemia: one of the factors leading to production of cytokines in liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6(Suppl 3):16.
-
- Enomoto N, Yamashina S, Kono H, Schemmer P, Rivera CA, Enomoto A, Nishiura T, Nishimura T, Brenner DA, Thurman RG. Development of a new, simple rat model of early alcohol-induced liver injury based on sensitization of Kupffer cells. Hepatology. 1999;29:1680–1689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

