Copper transportion of WD protein in hepatocytes from Wilson disease patients in vitro
- PMID: 11854914
- PMCID: PMC4695607
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.846
Copper transportion of WD protein in hepatocytes from Wilson disease patients in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To study the effect of copper transporting P-type ATPase in copper metabolism of hepatocyte and pathogenesis of Wilson disease (WD).
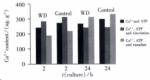
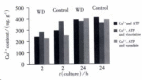
Methods: WD copper transporting properties in some organelles of the cultured hepatocytes were studied from WD patients and normal controls.These cultured hepatocytes were incubated in the media of copper 15 mg x L(-1) only, copper 15 mg x L(-1) with vincristine (agonist of P-type ATPase) 0.5mg x L(-1), or copper 15 mg x L(-1) with vanadate (antagonist of P-type ATPase) 18.39 mg x L(-1) separately. Microsome (endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus), lysosome, mitochondria, and cytosol were isolated by differential centrifugation. Copper contents in these organelles were measured with atomic absorption spectrophotometer, and the influence in copper transportion of these organelles by vanadate and vincristine were comparatively analyzed between WD patients and controls. WD copper transporting P-type ATPase was detected by SDS-PAGE in conjunction with Western blot in liver samples of WD patients and controls.
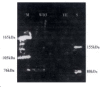
Results: The specific WD proteins (M(r)155,000 lanes) were expressed in human hepatocytes, including the control and WD patients. After incubation with medium containing copper for 2 h or 24 h, the microsome copper concentration in WD patients was obviously lower than that of controls, and the addition of vanadate or vincristine would change the copper transporting of microsomes obviously. When incubated with vincristine, levels of copper in microsome were significantly increased, while incubated with vanadate, the copper concentrations in microsome were obviously decreased. The results indicated that there were WD proteins, the copper transportion P-type ATPase in the microsome of hepatocytes. WD patients possessed abnormal copper transporting function of WD protein in the microsome, and the agonist might correct the defect of copper transportion by promoting the activity of copper transportion P-type ATPase.
Conclusion: Copper transportion P-type ATPase plays an important role in hepatocytic copper metabolism. Dysfunction of hepatocytic WD protein copper transportion might be one of the most important factors for WD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wilson disease at a single cell level: intracellular copper trafficking activates compartment-specific responses in hepatocytes.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30875-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.114447. Epub 2010 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20647314 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte GP73 expression in Wilson disease.J Hepatol. 2009 Sep;51(3):557-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.05.029. Epub 2009 Jun 25. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19596473 Free PMC article.
-
[A study of gene products encoded by Wilson disease gene].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2001 Apr;9(2):86-8. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2001. PMID: 11350685 Chinese.
-
Wilson disease.Gastroenterology. 2003 Dec;125(6):1868-77. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.05.010. Gastroenterology. 2003. PMID: 14724838 Review. No abstract available.
-
Wilson disease.Med Electron Microsc. 2002 Jun;35(2):61-6. doi: 10.1007/s007950200007. Med Electron Microsc. 2002. PMID: 12181646 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis of Wilson Disease and Its Phenotypes by Using Artificial Intelligence.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 20;11(8):1243. doi: 10.3390/biom11081243. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439909 Free PMC article.
-
Succinylation modification-mediated upregulation of Sp1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 15;15(1):660. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01533-9. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39548054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terada K, Schilsky ML, Miura N, Sugiyama T. ATP7B (WND) protein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;30:1063–1067. - PubMed
-
- Liang XLN (Eds) Neurological Genetics. Beijing: People’s Military Medicine Press; 2001. pp. 109–139.
-
- Ferenci P. Wilson's disease. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;31:416–425. - PubMed
-
- Liang X, Hou G, Chen R, Xu P, Huang F, Wang Y, Yan Z. [A study of gene products encoded by Wilson disease gene] Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2001;9:86–88. - PubMed
-
- Gollan JL, Gollan TJ. Wilson disease in 1998: genetic, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Hepatol. 1998;28 Suppl 1:28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

