Fas counterattack in cholangiocarcinoma: a mechanism for immune evasion in human hilar cholangiocarcinomas
- PMID: 11854917
- PMCID: PMC4695610
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.860
Fas counterattack in cholangiocarcinoma: a mechanism for immune evasion in human hilar cholangiocarcinomas
Abstract
Aim: To investigate FasL expression in hilar cholangiocarcinoma tissues and cultured cholangiocarcinoma cells, and to assess its ability to induce apoptosis.
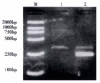
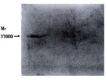
Methods: We studied the expression of FasL by human hilar cholangiocaroinomas tissues by immunohistochemistry, and the QBC939 cholangiocarcinoma cell line by RT-PCR, immunohistochemistry, and Western Blot. TUNEL and flow cytometry were used to detect apoptotic cells.
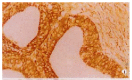
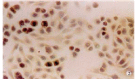
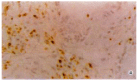
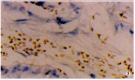
Results: Prevalent expression of FasL was detected in 39 resected hilar cholangiocarcinoma tissues. TUNEL staining disclosed a high level of cell death among lymphocytes infiltrating FasL positive areas of tumor. FasL mRNA and protein expressions in cholangiocarcinoma cells could induce Jurkat cells.
Conclusion: Hilar cholangiocarcinomas may elude immunological surveillance by inducing, via Fas/FasL system, the apoptosis of activated lymphocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The "Fas counterattack": a mechanism for immune evasion in human hilar cholangiocarcinomas].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002 May 10;82(9):606-9. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12133481 Chinese.
-
Cholangiocarcinomas express Fas ligand and disable the Fas receptor.Hepatology. 1999 Dec;30(6):1398-404. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300618. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 10573518
-
Up-regulation of fas ligand at early stages and down-regulation of Fas at progressed stages of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reflect evasion from immune surveillance.Hepatology. 2000 Oct;32(4 Pt 1):761-9. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.18192. Hepatology. 2000. PMID: 11003620
-
The Fas/Fas ligand system and cancer: immune privilege and apoptosis.Mol Biotechnol. 2003 Sep;25(1):19-30. doi: 10.1385/MB:25:1:19. Mol Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 13679631 Review.
-
Inhibition of Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptotic cell death of lymphocytes in vitro by circulating anti-Fas ligand autoantibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Feb;41(2):344-53. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199802)41:2<344::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-J. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. PMID: 9485093 Review.
Cited by
-
X-ray induced L02 cells damage rescued by new anti-oxidant NADH.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Aug;9(8):1781-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1781. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12918120 Free PMC article.
-
Trifluoperazine regulation of calmodulin binding to Fas: a computational study.Proteins. 2011 Aug;79(8):2543-56. doi: 10.1002/prot.23081. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Proteins. 2011. PMID: 21656570 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Role of Immune Checkpoint Regulators in Cholangiocarcinoma: A Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2021 May 19;10(10):2191. doi: 10.3390/jcm10102191. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34069452 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Fas/FasL pathway and the role of c-FLIP in primary culture of human cholangiocarcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 31;7(1):14419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14838-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29089545 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of vitamin E succinate on the expression of Fas and PCNA proteins in human gastric carcinoma cells and its clinical significance.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr 1;10(7):945-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i7.945. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15052671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Griffith TS, Brunner T, Fletcher SM, Green DR, Ferguson TA. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis as a mechanism of immune privilege. Science. 1995;270:1189–1192. - PubMed
-
- Bellgrau D, Gold D, Selawry H, Moore J, Franzusoff A, Duke RC. A role for CD95 ligand in preventing graft rejection. Nature. 1995;377:630–632. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S, Golstein P. The Fas death factor. Science. 1995;267:1449–1456. - PubMed
-
- Gu XH, Li QF, Wang YM. Expression of hepatocyte apoptosis and Fas/Fas L, in liver tissues of patients with hepatitis D. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:35–38.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

