Relationship between genotype and phenotype of flagellin C in Salmonella
- PMID: 11854918
- PMCID: PMC4695611
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.864
Relationship between genotype and phenotype of flagellin C in Salmonella
Abstract
Aim: To discover the relationship between the genotype and antigen serotype of flagellin C among Salmonella strains.
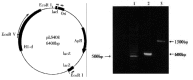
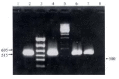
Methods: Fragment of Salmonella flagellin C in plasmid pLS408 was cloned, sequenced and compared with the corresponding sequence in other strains. Salmonella strains including two typhi strains, one paratyphoid strain, one enteritidis and one typhimurium strain were isolated from outpatients. Genome DNA was purified respectively from these clinical isolates, then the corresponding flagellin C fragment was amplified by polymerase chain reaction,and the amplification products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
Results: The cloned fragment includes 582 nucleotides encoding the variable region and partial conservative region of Salmonella flagellin C in plasmid pLS408. With comparison to the corresponding sequences reported previously, there is only a little difference from other strains with the same flagellar serotype in both nucleotide and amino acid level. Specific PCR products were amplified in Salmonella strains with flagellar serotype H-1-d including S. muenchen, typhi and typhimurium, but not in S. paratyphoid C or S. enteritidis strains.
Conclusion: In this experiment, the specificity of nucleotide sequence could be found in flagellin C central variable regions as it exists in flagellar serotypes in Salmonella. It may be helpful to developing a rapid, sensitive, accurate and PCR-based method to detect Salmonella strains with serotype H-1-d.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unique sequences in region VI of the flagellin gene of Salmonella typhi.Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1379-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00119.x. Mol Microbiol. 1989. PMID: 2615651
-
Multiplex PCR for distinguishing the most common phase-1 flagellar antigens of Salmonella spp.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Jun;42(6):2581-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2581-2586.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184437 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism of flagellin A gene in Helicobacter pylori.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Dec;7(6):783-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.783. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11854901 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a PCR system for the characterisation of Salmonella flagellin genes.Acta Vet Hung. 2005;53(2):163-72. doi: 10.1556/AVet.53.2005.2.2. Acta Vet Hung. 2005. PMID: 15959975
-
Comparative analysis of flagellin sequences from Escherichia coli strains possessing serologically distinct flagellar filaments with a shared complex surface pattern.J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5395-402. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5395-5402.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8366026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minamino T, González-Pedrajo B, Yamaguchi K, Aizawa SI, Macnab RM. FliK, the protein responsible for flagellar hook length control in Salmonella, is exported during hook assembly. Mol Microbiol. 1999;34:295–304. - PubMed
-
- Komoriya K, Shibano N, Higano T, Azuma N, Yamaguchi S, Aizawa SI. Flagellar proteins and type III-exported virulence factors are the predominant proteins secreted into the culture media of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Microbiol. 1999;34:767–779. - PubMed
-
- Soutourina O, Kolb A, Krin E, Laurent-Winter C, Rimsky S, Danchin A, Bertin P. Multiple control of flagellum biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: role of H-NS protein and the cyclic AMP-catabolite activator protein complex in transcription of the flhDC master operon. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:7500–7508. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

