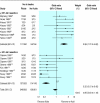
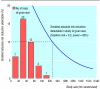
Does animal experimentation inform human healthcare? Observations from a systematic review of international animal experiments on fluid resuscitation
- PMID: 11859053
- PMCID: PMC1122396
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.324.7335.474
Does animal experimentation inform human healthcare? Observations from a systematic review of international animal experiments on fluid resuscitation
Figures
Comment in
-
Animal models can assist medicine in humans.BMJ. 2002 Jun 15;324(7351):1457. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7351.1457. BMJ. 2002. PMID: 12065282 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Croce P. Vivisection or science? An investigation into testing drugs and safeguarding health. London: Zed Books; 1999.
-
- Roberts I, Evans A, Bunn F, Kwan I, Crowhurst E. Normalising the blood pressure in bleeding trauma patients may be harmful. Lancet. 2001;357:385–387. - PubMed
-
- Bilynskyj MC, Errington ML, Velasco IT, Silva R. Effect of hypertonic sodium chloride (7.5%) on uncontrolled hemorrhage in rats and its interaction with different anesthetic procedures. Circulatory Shock. 1992;36:68–73. - PubMed
-
- Gross D, Landau EH, Klin B, Krausz MM. Quantitative measurement of bleeding following hypertonic saline therapy in ‘uncontrolled’ hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma. 1989;29:79–83. - PubMed
-
- Krausz MM, Kablan M, Rabinovici R, Klin B, Sherman Y, Gross D. Effect of injured vessel size on bleeding following hypertonic saline infusion in uncontrolled hemorrhagic shock in anesthetised rats. Circulatory Shock. 1991;35:9–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical