Reovirus-induced alterations in gene expression related to cell cycle regulation
- PMID: 11861824
- PMCID: PMC135961
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.6.2585-2594.2002
Reovirus-induced alterations in gene expression related to cell cycle regulation
Abstract
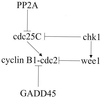
Mammalian reovirus infection results in perturbation of host cell cycle progression. Since reovirus infection is known to activate cellular transcription factors, we investigated alterations in cell cycle-related gene expression following HEK293 cell infection by using the Affymetrix U95A microarray. Serotype 3 reovirus infection results in differential expression of 10 genes classified as encoding proteins that function at the G(1)-to-S transition, 11 genes classified as encoding proteins that function at G(2)-to-M transition, and 4 genes classified as encoding proteins that function at the mitotic spindle checkpoint. Serotype 1 reovirus infection results in differential expression of four genes classified as encoding proteins that function at the G(1)-to-S transition and three genes classified as encoding proteins that function at G(2)-to-M transition but does not alter any genes classified as encoding proteins that function at the mitotic spindle checkpoint. We have previously shown that serotype 3, but not serotype 1, reovirus infection induces a G(2)-to-M transition arrest resulting from an inhibition of cdc2 kinase activity. Of the differentially expressed genes encoding proteins regulating the G(2)-to-M transition, chk1, wee1, and GADD45 are known to inhibit cdc2 kinase activity. A hypothetical model describing serotype 3 reovirus-induced inhibition of cdc2 kinase is presented, and reovirus-induced perturbations of the G(1)-to-S, G(2)-to-M, and mitotic spindle checkpoints are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reovirus-induced sigma1s-dependent G(2)/M phase cell cycle arrest is associated with inhibition of p34(cdc2).J Virol. 2001 Aug;75(16):7429-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7429-7434.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11462015 Free PMC article.
-
IkappaB kinase subunits alpha and gamma are required for activation of NF-kappaB and induction of apoptosis by mammalian reovirus.J Virol. 2007 Feb;81(3):1360-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01860-06. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17121808 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus-induced G(2)/M cell cycle arrest requires sigma1s and occurs in the absence of apoptosis.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(20):9562-70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9562-9570.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11000227 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus - possible therapy of cancer.Neoplasma. 2006;53(6):457-62. Neoplasma. 2006. PMID: 17167712 Review.
-
Molecular aspects of reovirus-host cell interaction.Microbiol Sci. 1988 Sep;5(9):265-70. Microbiol Sci. 1988. PMID: 3079190 Review.
Cited by
-
Reovirus-induced alteration in expression of apoptosis and DNA repair genes with potential roles in viral pathogenesis.J Virol. 2003 Aug;77(16):8934-47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.16.8934-8947.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12885910 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of apoptosis during reovirus infection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;289:1-24. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27320-4_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15791949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Biased Enrichment Does Not Improve Quantitative Proteomic Delineation of Reovirus T3D-Infected HeLa Cell Protein Alterations.Front Microbiol. 2012 Sep 20;3:310. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00310. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23024642 Free PMC article.
-
GeneChip resequencing of the smallpox virus genome can identify novel strains: a biodefense application.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;45(2):358-63. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01848-06. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17182757 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of reovirus bloodstream dissemination.Adv Virus Res. 2013;87:1-35. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407698-3.00001-6. Adv Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23809919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amon, A. 1999. The spindle checkpoint. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 9:69-75. - PubMed
-
- Barton, E. S., J. C. Forrest, J. L. Connolly, J. D. Chappell, Y. Liu, F. J. Schnell, A. Nusrat, C. A. Parkos, and T. S. Dermody. 2001. Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus. Cell 104:441-451. - PubMed
-
- Best, J. L., D. H. Presky, R. A. Swerlick, D. K. Burns, and W. Chu. 1995. Cloning of a full-length cDNA sequence encoding a cdc2-related protein kinase from human endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 208:562-568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

