The contribution of 2'-hydroxyls to the cleavage activity of the Neurospora VS ribozyme
- PMID: 11861903
- PMCID: PMC101248
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/30.5.1132
The contribution of 2'-hydroxyls to the cleavage activity of the Neurospora VS ribozyme
Abstract
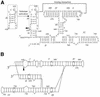
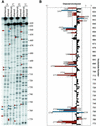
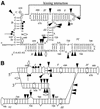
We have used nucleotide analog interference mapping and site-specific substitution to determine the effect of 2'-deoxynucleotide substitution of each nucleotide in the VS ribozyme on the self-cleavage reaction. A large number of 2'-hydroxyls (2'-OHs) that contribute to cleavage activity of the VS ribozyme were found distributed throughout the core of the ribozyme. The locations of these 2'-OHs in the context of a recently developed helical orientation model of the VS ribozyme suggest roles in multi-stem junction structure, helix packing, internal loop structure and catalysis. The functional importance of three separate 2'-OHs supports the proposal that three uridine turns contribute to local and long-range tertiary structure formation. A cluster of important 2'-OHs near the loop that is the candidate region for the active site and one very important 2'-OH in the loop that contains the cleavage site confirm the functional importance of these two loops. A cluster of important 2'-OHs lining the minor groove of stem-loop I and helix II suggests that these regions of the backbone may play an important role in positioning helices in the active structure of the ribozyme.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Varkud satellite ribozyme.RNA. 2004 Feb;10(2):151-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.5217104. RNA. 2004. PMID: 14730013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional equivalence of the uridine turn and the hairpin as building blocks of tertiary structure in the Neurospora VS ribozyme.J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 9;313(5):1013-9. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5119. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11700057
-
Rearrangement of substrate secondary structure facilitates binding to the Neurospora VS ribozyme.J Mol Biol. 2002 Dec 13;324(5):903-15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01151-8. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12470948
-
Identification of the catalytic subdomain of the VS ribozyme and evidence for remarkable sequence tolerance in the active site loop.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jul 12;320(3):443-54. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00521-1. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12096902
-
The structure and active site of the Varkud satellite ribozyme.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Nov;30(Pt 6):1170-5. doi: 10.1042/bst0301170. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12440998 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of SLV in SLI substrate recognition by the Neurospora VS ribozyme.RNA. 2008 Apr;14(4):736-48. doi: 10.1261/rna.824308. Epub 2008 Feb 26. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18314503 Free PMC article.
-
The Varkud satellite ribozyme.RNA. 2004 Feb;10(2):151-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.5217104. RNA. 2004. PMID: 14730013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of phosphate groups in the VS ribozyme-substrate interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Dec 1;32(21):6240-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh957. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15576350 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic and binding analysis of the catalytic involvement of ribose moieties of a trans-acting delta ribozyme.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 19;277(29):26508-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203468200. Epub 2002 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12015324 Free PMC article.
-
The NMR structure of the II-III-VI three-way junction from the Neurospora VS ribozyme reveals a critical tertiary interaction and provides new insights into the global ribozyme structure.RNA. 2015 Sep;21(9):1621-32. doi: 10.1261/rna.052076.115. Epub 2015 Jun 29. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26124200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quigley G.J. and Rich,A. (1976) Structural domains of transfer RNA molecules. Science, 194, 796–806. - PubMed
-
- Jack A., Ladner,J.E., Rhodes,D., Brown,R.S. and Klug,A. (1977) A crystallographic study of metal-binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. J. Mol. Biol., 111, 315–328. - PubMed
-
- Cate J.H., Gooding,A.R., Podell,E., Zhou,K., Golden,B.L., Kundrot,C.E., Cech,T.R. and Doudna,J.A. (1996) Crystal structure of a group I ribozyme domain: principles of RNA packing. Science, 273, 1678–1685. - PubMed

