A novel medium throughput quantitative competitive PCR technology to simultaneously measure mRNA levels from multiple genes
- PMID: 11861925
- PMCID: PMC101256
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/30.5.e20
A novel medium throughput quantitative competitive PCR technology to simultaneously measure mRNA levels from multiple genes
Abstract
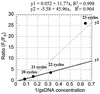
There is a great demand for technologies to simultaneously measure mRNA levels from multiple genes. Here we report a new quantitative competitive PCR technology and demonstrate simultaneous quantification of mRNA from multiple genes. First, a sequential 2-fold dilution series containing equal amounts of gene-specific standard DNAs for 10-12 genes is prepared. Second, the serially diluted standard DNAs are individually added to equal amounts of tissue-derived cDNA and amplified with gene-specific primers for 19-26 PCR cycles. Each gene/standard DNA pair is amplified individually. All amplified DNA products (n = 80) are resolved by one microplate array diagonal gel electrophoresis using 5% polyacrylamide. Changes in mRNA levels of approximately 15% can be detected by this technology. The mRNA levels from 10-12 genes were simultaneously quantified. mRNA levels were compared in RNA samples from rat liver, kidney and skeletal muscle. This quick, specific, sensitive, reproducible and yet inexpensive technique is ideal for simultaneously studying co-ordinate changes in mRNA levels from multiple genes.
Figures





References
-
- Guillausseau P.J., Tielmans,D., Virally-Monod,M. and Assayag,M. (1997) Diabetes: from phenotypes to genotypes. Diabetes Metab., 23 (suppl. 2), 14–21. - PubMed
-
- Shimkets R.A. and Lifton,R.P. (1996) Recent advances in the molecular genetics of hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens., 5, 162–165. - PubMed
-
- Drews J. (2000) Drug discovery: a historical perspective. Science, 287, 1960–1964. - PubMed
-
- Schena M., Shalon,D., Davis,R.W. and Brown,P.O. (1995) Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science, 270, 467–470. - PubMed
-
- Gibson U.E., Heid,C.A. and Williams,P.M. (1996) A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Genome Res., 6, 995–1001. - PubMed

