Signaling through the EGF receptor controls lung morphogenesis in part by regulating MT1-MMP-mediated activation of gelatinase A/MMP2
- PMID: 11865039
- PMCID: PMC2788991
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.115.4.839
Signaling through the EGF receptor controls lung morphogenesis in part by regulating MT1-MMP-mediated activation of gelatinase A/MMP2
Abstract
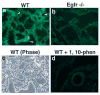
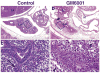
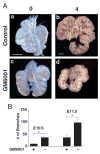
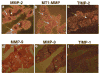
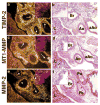
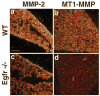
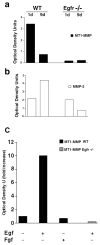
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during lung development require extracellular signaling factors that facilitate branching morphogenesis. We show here that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) originating in the mesenchyme are necessary for epithelial branching and alveolization. We found that the delayed lung maturation characterized by abnormal branching and poor alveolization seen in mice deficient in epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr(-/-)) is accompanied by aberrant expression of MMPs. By in situ zymography, the lungs from newborn Egfr(-/-) mice had low gelatinolytic activity compared with wildtype. Inhibition of MMPs in developing lungs in vivo or in vitro severely retarded morphogenesis. Egfr(-/-) mice had low expression of MT1-MMP/MMP14, which is a potent activator of gelatinase A/MMP2, in their lungs. Egf ligand increased MT1-MMP mRNA by tenfold in lung fibroblasts from wild type, but not from Egfr(-/-) mice. Extracts from lungs of Egfr(-/-) mice showed a tenfold reduction in active MMP-2, but only a slight decrease in proMMP-2 by zymography. At birth, MMP-2(-/-) mice had a lung phenotype characterized by abnormal lung alveolization which phenocopied that of Egfr(-/-) mice, albeit somewhat less severe. We conclude that proteolysis mediates epithelial/mesenchymal interactions during lung morphogenesis. From the phenotypes of the Egfr(-/-) mice, we identify MT1-MMP as a major downstream target of Egfr signaling in lung in vivo and in vitro. MT1-MMP is, in turn, necessary for activation of MMP-2, a mesenchymal enzyme that is required for normal lung morphogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander CM, Hansell EJ, Behrendtsen O, Flannery ML, Kishnani NS, Hawkes SP, Werb Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development. 1996;122:1723–1736. - PubMed
-
- Apte SS, Fukai N, Beier DR, Olsen BR. The matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) gene is structurally distinct from other MMP genes and is co-expressed with the TIMP-2 gene during mouse embryogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25511–25517. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Furuta Y, Rush MG, Henderson R, Winnier G, Hogan BL. Involvement of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mouse embryonic lung growth and morphogenesis. Development. 1997a;124:53–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

