The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 is regulated by Bmp signaling and c-Jun and modulates programmed cell death
- PMID: 11867524
- PMCID: PMC125884
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.966
The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 is regulated by Bmp signaling and c-Jun and modulates programmed cell death
Abstract
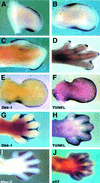
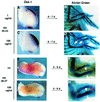
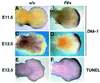
Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1) has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in a variety of assays and organisms. In this study, we show that expression of Dkk-1 overlaps significantly with the sites of programmed cell death in normal as well as mutant vertebrate limb development, and identify several of its upstream regulators, one of which is Bmp-4. Interestingly, Bmp-4 only activates Dkk-1 when it concomitantly induces apoptosis. Moreover, Dkk-1 is heavily up-regulated by UV irradiation and several other genotoxic stimuli. We further show that normal expression of Dkk-1 is dependent on the Ap-1 family member c-Jun and that overexpression of Dkk-1 enhances Bmp-triggered apoptosis in the vertebrate limb. Taken together, our results provide evidence for an important role of Dkk-1-mediated inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in response to different stress signals that all converge on the activation of c-Jun in vivo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bmp, Fgf and Wnt signalling in programmed cell death and chondrogenesis during vertebrate limb development: the role of Dickkopf-1.Int J Dev Biol. 2002;46(7):943-7. Int J Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12455632
-
Distinct WNT pathways regulating AER formation and dorsoventral polarity in the chick limb bud.Science. 1998 May 22;280(5367):1274-7. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5367.1274. Science. 1998. PMID: 9596583
-
Beta-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling in apical ectodermal ridge induction and FGF8 expression in normal and limbless mutant chick limbs.Dev Growth Differ. 2002 Aug;44(4):315-25. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-169x.2002.00647.x. Dev Growth Differ. 2002. PMID: 12175366
-
[Roles of the BMP family in pattern formation of the vertebrate limb].Clin Calcium. 2006 May;16(5):773-80. Clin Calcium. 2006. PMID: 16679618 Review. Japanese.
-
BMP signaling pathways in cartilage and bone formation.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2001;11(1-3):23-45. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2001. PMID: 11693963 Review.
Cited by
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein inhibits DKK1 expression through c-Jun-mediated inhibition of β-catenin activation of the DKK1 promoter in prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2014 May 8;33(19):2464-77. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.203. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23752183 Free PMC article.
-
REIC/Dkk-3 induces cell death in human malignant glioma.Neuro Oncol. 2008 Jun;10(3):244-53. doi: 10.1215/15228517-2008-016. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Neuro Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18443132 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention in Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 13;21(22):8573. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228573. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33202963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conditional inactivation of Fgfr1 in mouse defines its role in limb bud establishment, outgrowth and digit patterning.Development. 2005 Oct;132(19):4235-45. doi: 10.1242/dev.02001. Epub 2005 Aug 24. Development. 2005. PMID: 16120640 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt inhibitors Dkk1 and Sost are downstream targets of BMP signaling through the type IA receptor (BMPRIA) in osteoblasts.J Bone Miner Res. 2010 Feb;25(2):200-10. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.090806. J Bone Miner Res. 2010. PMID: 19874086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi-Yamada T., Fujimura-Kamada,K., Nishida,Y. and Matsumoto,K. (1999) Distortion of proximodistal information causes JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila wing. Nature, 400, 166–169. - PubMed
-
- Angel P., Hattori,K., Smeal,T. and Karin,M. (1988) The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP1. Cell, 55, 875–885. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A., Sibilia,M. and Wagner,E.F. (1999) Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nature Genet., 21, 326–329. - PubMed
-
- Bejsovec A. (2000) Wnt signaling: an embarrassment of receptors. Curr. Biol., 10, R919–R922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

