Protein 61K, encoded by a gene (PRPF31) linked to autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa, is required for U4/U6*U5 tri-snRNP formation and pre-mRNA splicing
- PMID: 11867543
- PMCID: PMC125353
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.1148
Protein 61K, encoded by a gene (PRPF31) linked to autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa, is required for U4/U6*U5 tri-snRNP formation and pre-mRNA splicing
Abstract
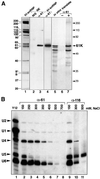
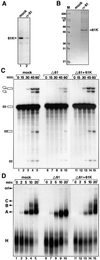
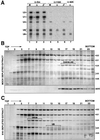
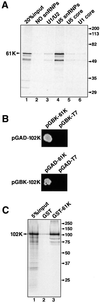
In each round of nuclear pre-mRNA splicing, the U4/U6*U5 tri-snRNP must be assembled from U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs, a reaction that is at present poorly understood. We have characterized a 61 kDa protein (61K) found in human U4/U6*U5 tri-snRNPs, which is homologous to yeast Prp31p, and show that it is required for this step. Immunodepletion of protein 61K from HeLa nuclear extracts inhibits tri-snRNP formation and subsequent spliceosome assembly and pre-mRNA splicing. Significantly, complementation with recombinant 61K protein restores each of these steps. Protein 61K is operationally defined as U4/U6 snRNP-specific as it remains bound to this particle at salt concentrations where the tri-snRNP dissociates. However, as shown by two-hybrid analysis and biochemical assays, protein 61K also interacts specifically with the U5 snRNP-associated 102K protein, indicating that it physically tethers U4/U6 to the U5 snRNP to yield the tri-snRNP. Interestingly, protein 61K is encoded by a gene (PRPF31) that has been shown to be linked to autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Thus, our studies suggest that disruptions in tri-snRNP formation and function resulting from mutations in the 61K protein may contribute to the manifestation of this disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The human U5 snRNP 52K protein (CD2BP2) interacts with U5-102K (hPrp6), a U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP bridging protein, but dissociates upon tri-snRNP formation.RNA. 2005 May;11(5):598-608. doi: 10.1261/rna.2300805. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15840814 Free PMC article.
-
The [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNP-specific 27K protein is a novel SR protein that can be phosphorylated by the snRNP-associated protein kinase.RNA. 1997 Apr;3(4):344-55. RNA. 1997. PMID: 9085842 Free PMC article.
-
The 20kD protein of human [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNPs is a novel cyclophilin that forms a complex with the U4/U6-specific 60kD and 90kD proteins.RNA. 1998 Feb;4(2):127-41. RNA. 1998. PMID: 9570313 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the U5 snRNP in spliceosome dynamics and catalysis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Dec;32(Pt 6):928-31. doi: 10.1042/BST0320928. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15506927 Review.
-
The assembly of a spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Nov;36(20):6482-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn658. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18854356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing and retinal degeneration.Clin Genet. 2013 Aug;84(2):142-9. doi: 10.1111/cge.12181. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Clin Genet. 2013. PMID: 23647439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conserved stem II of the box C/D motif is essential for nucleolar localization and is required, along with the 15.5K protein, for the hierarchical assembly of the box C/D snoRNP.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;22(23):8342-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.23.8342-8352.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12417735 Free PMC article.
-
Human U4/U6.U5 and U4atac/U6atac.U5 tri-snRNPs exhibit similar protein compositions.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(10):3219-29. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3219-3229.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11971955 Free PMC article.
-
PRPF mutations are associated with generalized defects in spliceosome formation and pre-mRNA splicing in patients with retinitis pigmentosa.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Jun 1;20(11):2116-30. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr094. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21378395 Free PMC article.
-
Disease mechanism for retinitis pigmentosa (RP11) caused by missense mutations in the splicing factor gene PRPF31.Mol Vis. 2008 Apr 18;14:683-90. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18431455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrens S.E. and Lührmann,R. (1991) Immunoaffinity purification of a [U4/U6·U5] tri-snRNP from human cells. Genes Dev., 5, 1439–1452. - PubMed
-
- Burge C.B., Tuschl,T. and Sharp,P.A. (1999) Splicing of precursors to mRNAs by the spliceosomes. In Gesteland,R.F. and Atkins,J.F. (eds), The RNA World. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 525–560.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

