A genetic screen for improved plasmid segregation reveals a role for Rep20 in the interaction of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes
- PMID: 11867551
- PMCID: PMC125903
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.1231
A genetic screen for improved plasmid segregation reveals a role for Rep20 in the interaction of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes
Abstract
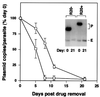
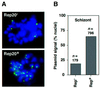
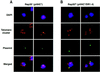
Bacterial plasmids introduced into the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum replicate well but are poorly segregated during mitosis. In this paper, we screened a random P.falciparum genomic library in order to identify sequences that overcome this segregation defect. Using this approach, we selected for parasites that harbor a unique 21 bp repeat sequence known as Rep20. Rep20 is one of six different repeats found in the subtelomeric regions of all P.falciparum chromosomes but which is not found in other eukaryotes or in other plasmodia. Using a number of approaches, we demonstrate that Rep20 sequences lead to dramatically improved episomal maintenance by promoting plasmid segregation between daughter merozoites. We show that Rep20(+), but not Rep20(-), plasmids co-localize with terminal chromosomal clusters, indicating that Rep20 mediates plasmid tethering to chromosomes, a mechanism that explains the improved segregation phenotype. This study implicates a direct role for Rep20 in the physical association of chromosome ends, which is a process that facilitates the generation of diversity in the terminally located P.falciparum virulence genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of some rep20 DNA fragments from the genome of the human malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum.J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2009 Aug;39(2):489-502. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19795756
-
Chromosomal polymorphism and sexual differentiation in Plasmodium.Parassitologia. 1993 Jul;35 Suppl:87-9. Parassitologia. 1993. PMID: 8233621
-
Frequent ectopic recombination of virulence factor genes in telomeric chromosome clusters of P. falciparum.Nature. 2000 Oct 26;407(6807):1018-22. doi: 10.1038/35039531. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11069183
-
Markers for population genetic analysis of human plasmodia species, P. falciparum and P. vivax.J Vector Borne Dis. 2003 Sep-Dec;40(3-4):78-83. J Vector Borne Dis. 2003. PMID: 15119076 Review.
-
Molecular approaches to monitor parasite genetic complexity in the transmission of Plasmodium falciparum malaria.Parassitologia. 2005 Jun;47(2):199-203. Parassitologia. 2005. PMID: 16252474 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein export marks the early phase of gametocytogenesis of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Jul;9(7):1437-48. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900479-MCP200. Epub 2010 Mar 22. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20332084 Free PMC article.
-
An essential contractile ring protein controls cell division in Plasmodium falciparum.Nat Commun. 2019 May 16;10(1):2181. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10214-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31097714 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the principles that govern mutually exclusive expression of Plasmodium falciparum clag3 genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 30;43(17):8243-57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv730. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26202963 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal DNA amplicons in antimalarial-resistant Plasmodium falciparum.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Apr;115(4):574-590. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14624. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33053232 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide nucleosome mapping of Plasmodium falciparum reveals histone-rich coding and histone-poor intergenic regions and chromatin remodeling of core and subtelomeric genes.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 16;10:610. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-610. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20015349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aslund L., Franzen,L., Westin,G., Persson,T., Wigzell,H. and Pettersson,U. (1985) Highly reiterated non-coding sequence in the genome of Plasmodium falciparum is composed of 21 base-pair tandem repeats. J. Mol. Biol., 185, 509–516. - PubMed
-
- Baruch D.I., Pasloske,B.L., Singh,H.B., Bi,X., Ma,X.C., Feldman,M., Taraschi,T.F. and Howard,R.J. (1995) Cloning the P. falciparum gene encoding PfEMP1, a malarial variant antigen and adherence receptor on the surface of parasitized human erythrocytes. Cell, 82, 77–87. - PubMed
-
- Bowman S. et al. (1999) The complete nucleotide sequence of chromosome 3 of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature, 400, 532–538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

